Clinical study of liver abscess
Abstract
Background: The aim of our study was to study general considerations, etiological and predisposing factors, symptoms and signs and various modalities of treatment of liver abscess.
Methods: We have taken 60 cases having proven liver abscess. All data collected from these cases was compared statistically. A predesigned proforma was used to collect this information for individual case. All selected cases were studied upto discharge regarding the type of liver abscess and treatment modalities.
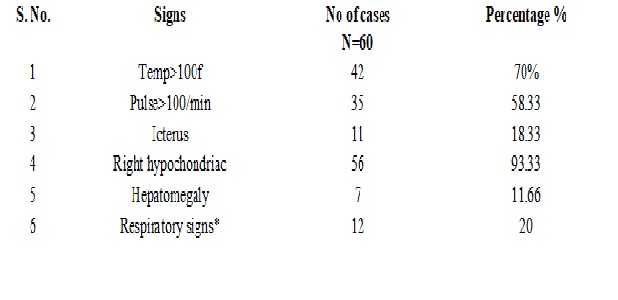
Results: Amoebic liver abscesses were more common than pyogenic liver abscesses. Liver abscesses were more common in 5th decade followed by 6th decade. Liver abscesses were more common in males than females; Diabetes mellitus (35%) and Alcoholism (23.3%) were the most common predisposing factor in our study. Single abscess was a finding in 71.66% and multiple abscess in 28.33% of patients.
Conclusion: The modern day ultrasound and other non-invasive imaging techniques had greatly revolutionized the diagnosis and management of the liver abscess.Conservative management with IV antibiotics and USG guided percutaneous aspiration of liver abscess are most frequent treatment modalities used now; with fewer complications.
Downloads
References
2. Mc cuskey RS, Reilly FD: variant of hepatic anatomy, dyanamic structure, and its regulation, Semin Liver disease 1993;13:45-18. American journal of surgery January 1973 Vol-125(1)70-79.
3. Davis A, Pawlowski ZS. Amoebiasis and its control. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(3):417-26.[pubmed]
4. Sharma MP, Ahuja V. Management of amebic liver abscess. Arch Med Res. 2000 Jul-Aug;31(4 Suppl):S4-5.[pubmed]
5. Johnson RD, Mueller PR, Ferrucci JT Jr, et al. Percutaneous drainage of pyogenic liver abscesses. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985 Mar;144(3):463-7. DOI:10.2214/ajr.144.3.463.[pubmed]
6. Rahimian J, Wilson T, Oram V, et al. Pyogenic liver abscess: recent trends in etiology and mortality. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Dec 1;39(11):1654-9. Epub 2004 Nov 9.[pubmed]
7. Seeto RK, Rockey DC. Pyogenic liver abscess. Changes in etiology, management, and outcome. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996 Mar;75(2):99-113.[pubmed]
8. Siu LK, Yeh KM, Lin JC, Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: a new invasive syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012 Nov;12(11):881-7. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70205-0.[pubmed]
9. Sabbaj J, Sutter VL, Finegold SM. Anaerobic pyogenic liver abscess. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Oct;77(4):627-38.[pubmed]
10. Ochsner A, DeBakey M, Murray S. Pyogenic abscess of the liver: II. An analysis of forty-seven cases with review of the literature. The American Journal of Surgery. 1938 Apr 1;40(1):292-319.
11. Powell SJ, MacLeod I, Wilmot AJ, Elsdon-Dew R. Metronidazole in amoebic dysentery and amoebic liver abscess. Lancet. 1966:1329-31.[pubmed]
12. Hanna RM, Dahniya MH, Badr SS, et al. Percutaneous catheter drainage in drug-resistant amoebic liver abscess. Trop Med Int Health. 2000 Aug;5(8):578-81.
13. Donovan AJ, Yellin AE, Ralls PW. Hepatic abscess. World J Surg. 1991 Mar-Apr;15(2):162-9.[pubmed]
14. Rajak CL, Gupta S, Jain S, Percutaneous treatment of liver abscesses: needle aspiration versus catheter drainage. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998 Apr;170(4):1035-9.[pubmed]
15. Barnes PF, De Cock KM, Reynolds TN, et al. A comparison of amebic and pyogenic abscess of the liver. Medicine (Baltimore). 1987 Nov;66(6):472-83.[pubmed]
16. Thompson Jr JE, Forlenza S, Verma R. Amebic liver abscess: a therapeutic approach. Reviews of infectious diseases. 1985 Mar 1;7(2):171-9.[pubmed]
17. Stain SC, Yellin AE, Donovan AJ, et al. Pyogenic liver abscess. Modern treatment. Arch Surg. 1991 Aug;126(8):991-6.[pubmed]


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

