“Clinical Profile and Outcome of Diabetic Foot Ulcer in South Indian Tertiary Care Centre”
Abstract
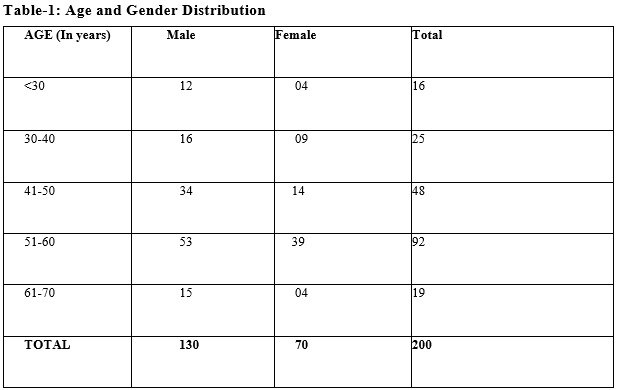
Aim: To study the clinical profile and outcome of diabetic foot ulcer in a Tertiary Care Centre. The clinical profile of 200 patients with diabetic foot ulcer was studied.
Methods: Patients with diabetic foot ulcer of both genders with age above 18 years willing to participate were included in the study. All patients were subjected to routine diabetic work up with Doppler study and X-ray foot to rule out bone involvement.
Results & discussion: The majority of patients with diabetic foot ulcers were of age group 51 to 60 years, male predominant, mostly with a duration of diabetes mellitus more than 6 years had intermittent claudication and most population with a single ulcer.
Conclusion: Our study gives important information that diabetic foot ulcer is more common among middle-aged people with male predominance which gives the importance of screening diabetic patients for neuropathy and peripheral vascular disease.
Downloads
References
Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010 Jan;87(1):4-14. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2009.10.007. Epub 2009 Nov 6. PMID: 19896746.
van Dieren S, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, Grobbee DE, Neal B. The global burden of diabetes and its complications: an emerging pandemic. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010 May;17 Suppl 1:S3-8. doi: 10.1097/01.hjr.0000368191.86614.5a. PMID: 20489418.
Reiber GE. Epidemiology of foot ulcers and amputation in the diabetic foot. In: Bowker J, Pfeifer M, editors. The diabetic foot. St. Louis: Mosby; 2001. p.12–32.Pubmed.
Adam DJ, Raptis S, Fitridge RA. Trends in the presentation and surgical management of the acute diabetic foot. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2006 Feb;31(2):151-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2005.05.039. Epub 2005 Jul 14. PMID: 16023389.
El-Maadawy G, Sabry A, Mohi Elden H, et al. Different procedures in the management of diabetic foot infections. Trends Med Res.2010;5:16–30.DOI:10.3923/tmr.2010.16.30.
Waspadji S. Kaki diabetik: kaitannyadenganneuro- patidiabetik. In: Djokomoeljanto R, DarmonoSuhartonoT, editors. Kaki diabetik: patogenesisdanpenatalaksanaan. Semarang: Diponegoro University Press; 1996. p.E1–E23.Pubmed.
Khosla HL, Caroli RK, Bahl AL. Peripheral vascular disease in diabetes mellitus. A clinical study. Indian J Med Sci. 1966 Oct;20(10):698-703. PMID: 5957765.
Ahuja MMS, Kumar V. Diabetes mellitus in the Indian science: Progressin Clinical Medical(Ed.)Ahuja MMS. Arnold Hernemann New Delhi1976.
Dey AB, Samal KC, Tripathy BB, Mohanty PC, Misra G, Misra NC. Observations on diabetic foot. J Indian Med Assoc. 1983 Sep;81(5-6):82-5. PMID: 6674336.
Decroli E, Karimi J, Manaf A, et al. Profil ulkusdiabetik pada penderitarawatinap di bagianpenyakit dalam RSUP Dr. M. Djamil Padang. Maj KedoktIndones.2008;58:3–7.
Reiber GE, Lipsky BA, Gibbons GW. The burden of diabetic foot ulcers. Am J Surg. 1998 Aug;176(2A Suppl):5S-10S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(98)00181-0. PMID: 9777967.
Sussman KE. Juvenile type Diabetes and its complications. Springfield.1971;348-377.
KEIDING NR, ROOT HF, MARBLE A. Importance of control of diabetes in prevention of vascular complications. J Am Med Assoc. 1952 Nov 8;150(10):964-9. doi: 10.1001/jama.1952.03680100006003. PMID: 12990325.
Garcia M, McNamara P, Gordon T, Kannel WB. Cardiovascular complications in diabetics. Adv Metab Disord. 1973;2:Suppl 2:493-9. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027362-1.50057-1. PMID: 4720380.
Rayman G, Hassan A, Tooke JE. Blood flow in the skin of the foot related to posture in diabetes mellitus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986 Jan 11;292(6513):87-90. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6513.87. PMID: 3080102; PMCID: PMC1339107.
Edmonds ME. The neuropathic foot in diabetes. Part I: Blood flow. Diabet Med. 1986 Mar;3(2):111-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1986.tb00720.x. PMID: 2951150.
Janka HU, Standl E, Mehnert H. Peripheral vascular disease in diabetes mellitus and its relation to cardiovascular risk factors: screening with the doppler ultrasonic technique. Diabetes Care. 1980 Mar-Apr;3(2):207-13. doi: 10.2337/diacare.3.2.207. PMID: 7389542.
Pirart J. Diabète et complications dégénératives. Présentation d'une étude prospective portant sur 4400 cas observés entre 1947 et 1973 (troisième et dernière partie) [Diabetes mellitus and its degenerative complications: a prospective study of 4,400 patients observed between 1947 and 1973 (3rd and last part) (author's transl)]. Diabete Metab. 1977 Dec;3(4):245-56. French. PMID: 598565.
Beach KW, Strandness DE Jr. Arteriosclerosis obliterans and associated risk factors in insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):882-8. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.882. PMID: 7429028.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

