Supracutaneous plating in tibial metadiaphyseal fractures with compromised soft tissue using LCP as an external fixator
Abstract
Introduction: Tibial meta-diaphysealfractures are challenging injuries because of subcutaneous anteromedial surface of bone and frequent soft tissue complications. Ideal management requires stable fixation with minimal soft tissue handling. Locking compression plate (LCP) applied as an external fixator fulfills these criteria and can be an important tool in the armamentarium of an orthopaedic surgeon. Objective of the study is to evaluate the result of this technique.
Methods: 23 patients with meta-diaphyseal fractures of tibia with compromised soft tissue treated by this technique were evaluated retrospectively interms of union, maintenance of reduction, complications and final outcome using KSS (Knee society scoring) for proximal fractures and AOFAS (AO Ankle and Foot scoring) for distal fractures. Average follow up duration was 9.4 months (6-14 months).
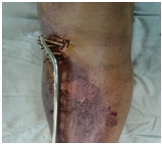
Results: There were fifteen males, eight females with fourteen open fractures and nine cases of closed fractures with tscherne grade 2 or 3 soft tissue injury. Five fractures were in proximal tibia and eighteen were in distal tibia, all fractures united with an average of 21.7 weeks period maintaining acceptable reduction. There were 3 cases of infection, one deep and two superficial treated successfully by debridement and antibiotics. Average knee society scores were 74 and 78.6 for open and close proximal metadiaphyseal fractures respectively. Average AOFAS scores were 81.9 and 84 for open and close distal tibial metadiaphyseal fractures respectively.
Conclusion: we found this technique to be more biological, simple to do surgery, effective in maintaining reduction till union, more patient friendly in comparison to traditional large, bulkyfixators and with minimal complications.
Downloads
References
2. Young MJ, Barrack RL. Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev. 1994 Feb;23(2):149-54.[pubmed]
3. Philip A. McCann, Jackson M, Steve T et al. Complication of definitive open reduction and internal fixation in tibial pilon fractures. Intl. Orthop2011 Mar; 35(3): 413–418.
4. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002 Nov;84(8):1093-110.[pubmed]
5. Borrelli J Jr, Prickett W, Song E, et al. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma. 2002 Nov-Dec;16(10):691-5.[pubmed]
6. McCann PA, Jackson M, Mitchell ST, et al. Complications of definitive open reduction and internal fixation of pilon fractures of the distal tibia. Int Orthop. 2011 Mar;35(3):413-8. doi: 10.1007/s00264-010-1005-9. Epub 2010 Mar 30.[pubmed]
7. Luo P, Xu D, Wu J, et al. Locked plating as an external fixator in treating tibial fractures: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(49):e9083. doi: 10.1097/MD. 0000000000009083.[pubmed]
8. Gupta P1, Tiwari A1, Thora A, et al. Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for Proximal and Distal Fractures of The Tibia: A Biological Approach. Malays Orthop J. 2016 Mar;10(1):29-37. doi: 10.5704/MOJ.1603.006.[pubmed]
9. Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, et al. Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures.x Int Orthop. 2008 Oct;32(5):697-703. Epub 2007 Jun 16.
10. Marti RK, van der Werken C. he AO-plate for external fixation in 12 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1991 Feb;62(1):60-2.[pubmed]
11. Kloen P. Supercutaneous plating: use of a locking compression plate as an external fixator. J Orthop Trauma. 2009 Jan;23(1):72-5. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e31818f8de4.[pubmed]
12. Tulner SA, Strackee SD, Kloen P. et al. Metaphyseal locking compression plate as an external fixator for the distal tibia. Int Orthop. 2012 Sep;36(9):1923-7. doi: 10.1007/s00264-012-1585-7. Epub 2012 Jun 1.
13. Gupta SKV, Parimala SP. Supracutaneous Locking Compression Plate for Grade I & II Compound Fracture Distal Tibia—A Case Series Open Journal of Orthopedics. 2013, 3, 106-109
14. Qiu XS, Yuan H, Zheng X, et al. Locking plate as a definitive external fixator for treating tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue envelop. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014 Mar;134(3):383-8. doi: 10.1007/s00402-013-1916-1. Epub 2013 Dec 22.[pubmed]
15. Panda SS, Panda D, Suri N. Supracutaneous plating –use of LCP as an external fixator for intra articular compound fractures. International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 8:62-67
16. Shrinivas P, Binayak R. A study of Locking compression plate as external fixator in the definitive management of open diaphyseal fractures of tibia in adults. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences 2019 Jan; 18(1):7-13
17. Zhang J, Ebraheim N, Li M, et al. External fixation using femoral less invasive stabilization system plate in tibial proximal metaphyseal fracture. Clin Orthop Surg. 2015 Mar;7(1):8-14. doi: 10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.8. Epub 2015 Feb 10.[pubmed]
18. Zhang J, Ebraheim NA, Li M, et al. External Fixation Using a Locking Plate: A Reliable Way in Treating Distal Tibial Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2015 Nov;29(11):e454-8. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000377.[pubmed]
19. Ahmad M, Nanda R, Bajwa AS, et al. Biomechanical testing of the locking compression plate: when does the distance between bone and implant significantly reduce construct stability? Injury. 2007 Mar;38(3):358-64. Epub 2007 Feb 12.[pubmed]
20. Zhang J, Ebraheim N, Li M, et al. External fixation using locking plate in distal tibial fracture: a finite element analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015 Aug;25(6):1099-104. doi: 10.1007/s00590-015-1604-7. Epub 2015 Feb 21.[pubmed]
21. Wei Liu, Lihui Y, Xiaochuan K et al. Stiffness of the locking compression plate as an external fixator for treating distal tibial fractures: a biomechanics study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017; 18: 26.
22. Kanchanomai C, Phiphobmongkol V. Biomechanical evaluation of fractured tibia externally fixed with an LCP. J Appl Biomech. 2012 Nov;28(5):587-92. Epub 2012 May 9.
23. Ang BFH, Chen JY, Yew AKS, et al. Externalised locking compression plate as an alternative to the unilateral external fixator: a biomechanical comparative study of axial and torsional stiffness. Bone Joint Res. 2017 Apr;6(4):216-223. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.64.2000470.[pubmed]
24. Win MT, Yasser M, Tint L et al. Supracutaneous plate: A comparable alternative to external fixator in the treatment of open fracture. IJOS 2018; 4(2): 959-962.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

