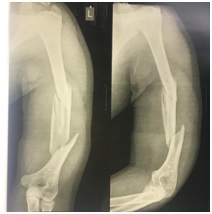
Study of radiological and clinical outcomes by using Anterior Bridge Plating (ABP) for humerus shaft fractures
Abstract
Background: The humerus can be considered the most versatile bone in the human body. Plating can be performed using a classic open approach or minimally invasive methods. Many humeral fractures can be successfully managed conservatively due to the wide range of acceptability. Anterior bridge plating (ABP) which utilizes the minimally invasive approach popularly known as the minimally invasive Percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) technique can be said to be the latest entrant in this list. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the efficacy of anterior bridge plating.
Method: The study was carried out from April 2015 to December 2015 involving 15 patients who met the selection criteria and were operated at the tertiary care centre. Informed consent was obtained from all the patients for use of their clinical and imaging data. The assessment of the patients was done based on functional and radiological outcomes periodically.
Result: Majority of patients belongs to age group 18-25 years (53.3%). The average age is 27.4 years. Majority of side of injury were found right side (80%). Most of cases of extent of displacement of fractures were 2-5 cms (80%).
Conclusion: In conclusion anterior bridge plating (ABP) is very good technique in treating midshaft humeral fractures with minimal soft tissue dissection, smaller scars, and early return to overhead activities.
Downloads
References
2. Sarmiento A, Waddell JP, Latta LL. Diaphyseal humeral fractures: treatment options. Instr Course Lect. 2002;51:257-69.[pubmed]
3. Lee HJ, Oh CW. Operative treatment of humerus shaft fracture: conventional open plating or minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Korean Fract Soc. 2012;25(2):155-62.
4. Meekers FS, Broos PL. Operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures. The Leuven experience. Acta Orthop Belg. 2002 Dec;68(5):462-70.[pubmed]
5. Chen F, Wang Z, Bhattacharyya T. Outcomes of nails versus plates for humeral shaft fractures: a Medicare cohort study. J Orthop Trauma. 2013 Feb;27(2):68-72. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e31824a3e66.[pubmed]
6. Chen AL, Joseph TN, Wolinksy PR, et al. Fixation stability of comminuted humeral shaft fractures: locked intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation. J Trauma. 2002 Oct;53(4):733-7.[pubmed]
7. Spiguel AR, Steffner RJ. Humeral shaft fractures. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2012 Sep;5(3):177-83. doi: 10.1007/s12178-012-9125-z.[pubmed]
8. Lin J. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures with humeral locked nail and comparison with plate fixation. J Trauma. 1998 May;44(5):859-64.[pubmed]
9. Zhiquan A, Bingfang Z, Yeming W, et al. Minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis (MIPO) of middle and distal third humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2007 Oct;21(9):628-33.[pubmed]
10. Ziran BH, Belangero W, Livani B, et al. Percutaneous plating of the humerus with locked plating: technique and case report. J Trauma. 2007 Jul;63(1):205-10.[pubmed]
11. Livani B, et al. Is MIPO in humeral shaft fractures really safe? Postoperative ultra sonographic evaluation. Int Orthop, 2009; 33:1719-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0616-x
12. Concha JM, Sandoval A, Streubel PN. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fractures: are results reproducible? Int Orthop. 2010 Dec;34(8):1297-305. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0893-z. Epub 2009 Oct 21.[pubmed]
13. Shetty MS, Kumar MA, Sujay K, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for humerus diaphyseal fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2011 Nov;45(6):520-6. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.87123.
14. Kim JW, Oh CW, Byun YS, et al. A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Orthop Trauma. 2015 Apr;29(4):189-94. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000232.[pubmed]
15. Wang C, Li J, Li Y, Dai G, et al. Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture advantageous compared with the conventional open technique? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015 Nov;24(11):1741-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.07.032.[pubmed]
16. Malhan S, Thomas S, Srivastav S, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using a locking compression plate for diaphyseal humeral fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2012 Dec;20(3):292-6. DOI:10.1177/230949901202000305.[pubmed]
17. Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Tscherne H. Distal femoral fractures. Transarticular reconstruction, percutaneous plate osteosynthesis and retrograde nailing. Unfallchirurg. 1996 Jan;99(1):2-10.[pubmed]
18. Sharma J, Jain A, Jain P G, Upadhyaya P. Anterior Bridge Plating with Mini Incision MIPO Technique for Humerus Diaphyseal Fractures. Ind. J. of Ortho. Surgery.2015;1(3):171-175.
19. Paulo Roberto Vilaca Jr., Marcelo Koh Uezumi. Anterior minimally invasive bridge-plate technique for treatment of humeral shaft non union: J Orthopaed Traumatol 2012;13:211–216.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

