Colonoscopic assessment of large bowel diseases and its effectiveness
Abstract
Introduction: Colonoscopy, for any suspected colonic disease is the first line of investigation. The spectrum of colonic diseases varies from benign to malignant lesions, of which the incidence and mortality differ across the world due to differences in risk factors. Colonoscopy is carried out for diagnostic and/or therapeutic purposes.
Materials and Methods: It was a hospital based cross sectional study conducted in Dr. Shankarrao Chavan Govt. Medical College, Nanded, during study period of May 2016 to December 2017 on 104 patients presented with clinical features of large bowel diseases.
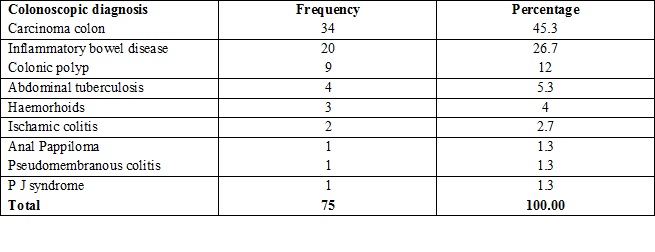
Results: The mean age of the patients was 45.59 ± 18.46 years (range 5 – 95). Males constituted 64.4% patients while females were 35.6%. On colonoscopy most common suspected diagnosis was carcinoma rectum (45.3%), followed by inflammatory bowel disease (26.7%) and rectal polyp (12%). Most of the lesions were found overall in rectum (49.5 %) followed by sigmoid colon (16.8%) and caecum (12.6%).
Conclusion: Colonoscopy is a safe and simple procedure helps in locating various lesions in the entire colon and confirming the diagnosis by histopathology. Colonoscopy helps not only in the diagnosis but also in the treatment and follow up of the patient especially in the colonic diseases like colonic cancer and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Downloads
References
2. Abilash SC, Shreelakshmidevi S. Histopathological Interpretation of Colonic MucosalBiopsies with Clinical Correlation: A Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital Kerala. Annalsof Pathology and Laboratory medicine. 2017; 4(5):567-572.DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1534.
3. Haggar FA, Boushey RP. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009 Nov;22(4):191-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1242458.[pubmed]
4. Kedia S, Ahuja V. Epidemiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in India: The Great Shift East. Inflamm Intest Dis. 2017 Nov;2(2):102-115. doi: 10.1159/000465522. Epub 2017 Apr 8.[pubmed]
5. Kamalesh NP, Prakash K, Pramil K, et al. Prevalence and patterns of diverticulosis in patients undergoing colonoscopy in a southern Indian hospital. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2012 Dec;31(6):337-9. doi: 10.1007/s12664-012-0222-0. Epub 2012 Aug 17.
6. Wickramasinghe DP, Samaranayaka SF, Lakmal C, Mathotaarachchi S, Keppetiyagama C. Types and Patterns of Colonic Polyps Encountered at a Tertiary Care Center in a Developing Country in South Asia. Analytical Cellular Pathology.2014:1-4.doi: 10.1155/2014/248142
7. Cappell MS, Friedel D. The role of sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy in the diagnosis and management of lower gastrointestinal disorders: endoscopic findings, therapy and complication. Medical Clinics of North America 2002; 86 (6):1253-1288.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-7125(02)00077-9
8. Bowles R, Leicester E, Swarbrick CB, Williams C, Romaya O, Epstein: Identification and management of polyps diagnosed at colonoscopy. Gut. 2001;48(Suppl I-034):10-14.10.1136/gut.48.suppl_1.A10PMCID: PMC1766846
9. Karve SH, Vidya K, Shivarudrappa AS, Prakash CJ. The Spectrum of colonic lesions:A Clinico-pathological study of colonic biopsies. Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology. 2015; 2(4):189-209. DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2015.00018.6
10. Rex DK, Schoenfeld PS, Cohen J, Pike IM, Adler DG. Quality indicators forcolonoscopy. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2015; 81(1):31-53.doi: 10.1016/j.tgie.2013.02.005. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.07.058. Epub 2014 Dec 2.
11. Schoenfeld PS, Cohen J. Quality indicators for colorectal cancer screening forcolonoscopy. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 15(2):59-68.doi: 10.1016/j.tgie.2013.02.005. PMID: 24098071PMCID: PMC3790322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tgie.2013.02.005
12. Siddique I, Mohan K, Hasan F, Memon A, Patty I, Al-Nakib B. Appropriateness ofindication and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: First report based on the 2000guidelines of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. World Journal of Gastroenterology 2005; 11(44):7007-7013.doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.7007.[pubmed]
13. Sonnenberg A, Delcò F, Inadomi JM. Cost-effectiveness of colonoscopy in screening for colorectal cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2000 Oct 17;133(8):573-84.[pubmed]
14. Thomas-Gibson C, Thapar S, Shah G and Saunders B. Colonoscopy at a combined district general hospital and specialist endoscopy unit: lessons from 505 consecutive examinations. Journal of Royal Society of Medicine. 2002; 95(4): 194 - 197.PMID: 11934910.
15. Fisher DA, Maple JT, Cash BD, Decker GA, Evans JA, Fanelli RD, Jain R.Complications of Colonoscopy. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2011; 74(4):744-752. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2011.07.025
16. Greene FL, Livstone EM, Troncale FJ. The role of fibreoptic colonoscopy in the diagnosis of colonic and rectal diseases. Conn Med.1973; 37:439-42.[pubmed]
17. Bafandeh Y, Yazdanpanah F. Distribution pattern of colorectal diseases based on2300 total colonoscopies. Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench 2017; 10(2): 90-96. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22037/ghfbb.v0i0.895.PMID:28702131.
18. Rajbhandari M, Karmacharya A, Khamal K, Dhakal P, Shreshtha R. Histomorphological profile of colonoscopic biopsies and pattern of colorectal carcinomas in Kavre district. Kathmandu University Medical Journal. 2013; 43(3):196-200.https://doi.org/10.3126/kumj.v11i3.12503
19. Mahamoud G, Kabbaj N, Amrani L, Serraj I, Guedira M, Nya M, Chaoui Z, Amrani N.A Moroccan Experience with Colonoscopy - A Review of 1157 Cases. Arab Journal of Gastroenterology. 2008; 9(3): 82-84. http://www.arabjg.eg.net/2008_part3/article_no.7.pdf.
20. Thakeb F, Zakaria S, Miland M, Khalil A, Hunter S and El Robby A. A review of 10 year experience with colonoscopy. In: Zakaria S, Thakeb F (eds).Gastrointestina Enodscopy: An Egyptian View, (1st edn). National Library Legal Deposit. 1987; p 83-95.
21. Cai J, Yuan Z, Zhang S. Abdominal pain, diarrhoea, constipation- -which symptom ismore indispensable to have a colonoscopy? International Journal of Clinical And Experimental Pathology.2015; 8(1):938-942.
22. Birajdar PB, Thakur SS, Bafana PN. Role of colonoscopy in the management of lowergastrointestinal disorders: Diagnostic and Therapeutic. International Journal of nnovative Research in Medical Science. 2017; 2(8):1182-1190. DOI https://doi.org/10.23958/ijirms/vol02-i08/16
23. Benevides GD, Marques dos santos CH. Colonoscopy in the diagnosis of acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Journal of Coloproctology. 2016;36(4):185-188.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcol.2016.04.016


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

