Diagnostic laparoscopy in right iliac fossa pain
Abstract
Background: Abdominal pain is a common problem in both males and females. Early Diagnosis is needed to rule out life threatening emergencies. Diagnosticlaparoscopy is very much useful in giving proper treatment and avoiding negative laparotomies.
Aims & objectives: To study the use of laparoscope in patients with acute or chronic right iliac fossa pain, to diagnose and confirm conditions like acute appendicitis, abscess, perforation, mass formation, etc. where clinical and imaging studies are inconclusive.
Materials & Methods: Place: Department of General surgery, Melmaruvathur Adhiparasakthi Institute of Medical Science and Research, Melmaruvathur.
Period of study: June 2017 to January 2018.
Material: All patients with right iliac fossa pain in the ages between ten years and seventy years were included in this study.
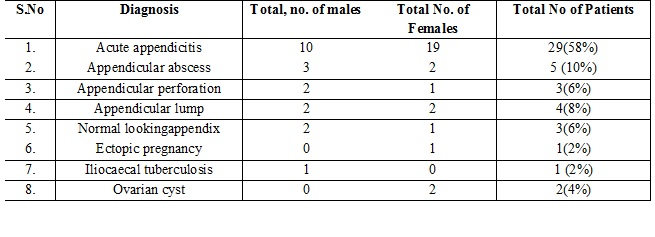
Results: Total 50 patients were included in this prospectivestudy. 29 patients (58%) were found to have acute appendicitis. Complicated appendix cases like mass formation, perforated appendix, appendicular abscess was found in 12 patients (24%). Normal looking appendix was found in 3 patients (6%). Non appendix lesions were found in 6 patients (12%).
Conclusions: The best approach in right iliac fossa pain is to do diagnostic laparoscopy and proceed, rather than going for open appendisectomy. Diagnostic laparoscopy gives all benefits of minimal invasive surgery. Not much of pain, shorter period of hospitalization, small scars, low infection rates and most importantly, accurate diagnosis and the correct treatment of most of the intra abdominalconditionsarethe gifted things.
Downloads
References
2. Ning N, Xia SY, Ma B, et al. [Application of laparoscopic technique in acute abdomen of gastrointestinal surgery]. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Oct;16(10):960-2.
3. Drăghici I, Drăghici L, Popescu M, et al. Laparoscopic exploration in pediatric surgery emergencies. J Med Life. 2010 Jan-Mar;3(1):90-5.[pubmed]
4. Sauerland S, Agresta F, Bergamaschi R, et al. Laparoscopy for abdominal emergencies: evidence-based guidelines of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery. Surg Endosc. 2006 Jan;20(1):14-29. Epub 2005 Oct 24.DOI:10.1007/s00464-005-0564-0.[pubmed]
5. Agrusa A, Romano G, Di Buono G, et al. Laparoscopic approach in abdominal emergencies: a 5-year experience at a single center. G Chir. 2012 Nov-Dec;33(11-12):400-3.
6. Reiertsen O, Trondsen E, Bakka A, Andersen OK, LarsenS, Rosseland AR. Prospective nonrandomized study of conventional versus laparoscopic appendectomy. World J Surg. 1994; 18:411-415. (Pub Med)
7. Gajalakshmi CK, Krishnamurthi S, Ananth R, et al. Cervical cancer screening in Tamilnadu, India: a feasibility study of training the village health nurse. Cancer Causes Control. 1996 Sep;7(5):520-4.[pubmed]
8. Golash V, Willson PD. Early laparoscopy as a routine procedure in the management of acute abdominal pain: a review of 1,320 patients. Surg Endosc. 2005 Jul;19(7):882-5. Epub 2005 May 12.DOI:10.1007/s00464-004-8866-1.[pubmed]
9. Gaitán HG, Reveiz L, Farquhar C, et al. Laparoscopy for the management of acute lower abdominal pain in women of childbearing age. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 22;(5):CD007683. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007683.pub3.
10. Lobe ET. Laparoscopic surgery in children. Currprobl. Surg. 1998: 35: 869-948. (Pub Med)
11. Parteckev L et al. Appendicitis : A pro for laparoscopic appendectomy as the standard procedure for acute appendicitis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2010 Nov; 395(8): 1069-76. Dol:10.1007/s00423-009-0567-8. Epub 2009 Nov 19.
12. Talat N, Afzal M, Ahmad S, et al. Role of diagnostic laparoscopy in evaluation and treatment of chronic abdominal pain in children. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2016 Jan-Mar;28(1):35-8.[pubmed]
13. van den Broek WT, Bijnen AB, van Eerten PV, et al. Selective use of diagnostic laparoscopy in patients with suspected appendicitis. Surg Endosc. 2000 Oct;14(10):938-41.[pubmed]
14. Phillips AW, Jones AE, Sargen K. Should the macroscopically normal appendix be removed during laparoscopy for acute right iliac fossa pain when no other explanatory pathology is found? Surg LaparoscEndoscPercutan Tech. 2009 Oct;19(5):392-4. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e3181b71957.[pubmed]
15. Greason KL, Rappold JF, Liberman MA. Incidental laparoscopic appendectomy for acute right lower quadrant abdominal pain. Its time has come. Surg Endosc. 1998 Mar;12(3):223-5.[pubmed]
16. Chiarugi M, Buccianti P, Decanini L, et al. What you see is not what you get". A plea to remove a 'normal' appendix during diagnostic laparoscopy. Acta Chir Belg. 2001 Sep-Oct;101(5):243-5.[pubmed]
17. Borgstein PJ, Gordijn RV, Eijsbouts QA, et al. Acute appendicitis--a clear-cut case in men, a guessing game in young women. A prospective study on the role of laparoscopy. Surg Endosc. 1997 Sep;11(9):923-7.[pubmed]
18. Akbar F, Yousuf M, Morgan RJ, et al. Changing management of suspected appendicitis in the laparoscopic era. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010 Jan;92(1):65-8. doi: 10.1308/003588410X12518836439920.[pubmed]


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

