Locking compression plate for proximal humerus fracture: A functional outcome analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Proximal humerus fractures are often the result of a fall in an osteoporotic patient, but can also occur in young adults due to high energy trauma. They account for 4-5% of all fractures. Over the past few decades, several operative techniques have been described for the treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Currently locking compression plate is gaining popularity. This plate combines the feature of compression of regular plate and locking into one system.
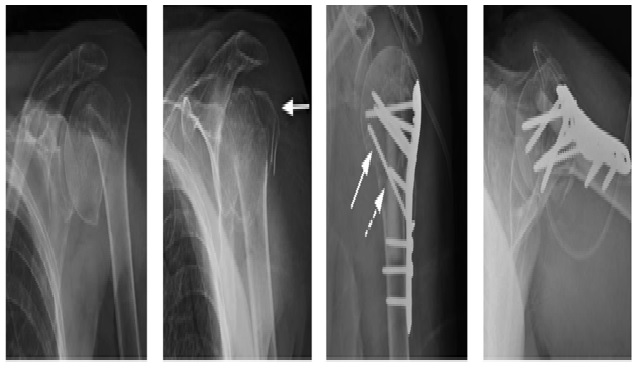
Methods: The present study is a prospective study conducted at Department of Orthopedics, S.B.H.GMC Dhule over a period of 2 years from March 2015 to March 2017. Total 34 patients of proximal humerus fracture which were admitted in Orthopedics ward were included in the present study. X ray of proximal humerus was taken and the fractures were classified according to Neer’s classification. All the patients were subjected for open reduction and internal fixation withlocking compression plate i.e. PHILOS (Proximal Humerus Interlocking System).Fracture approached through anterior deltopectoral approach. Post operatively patients were mobilized as early as possible. Patients were followed up and functional outcome was assessed using Neer’s functional scoring system. Mean follow up was 1 year.
Results: All the 34 patients of displaced proximal humerus were operated by open reduction and internal fixation using locking compression plate (PHILOS). Among these 19 (55.88%) were males and 15 (44.12%) were females. Age of patients ranged from 29 to 75 years with mean of 52 years. All fractures were classified according to Neer’s functional scoring system. 8 (23.5%) patientswere typeII, 11(32.35%) were type III and 15 (44.11%) were type IV. Functional outcome was assessed using Neer’s functional scoring system. According to Neer’s score 60% of our patients had satisfactory to excellent results and 40% of the patients had unsatisfactory to poor results.
Conclusion: According to present study results of locking compression plate, PHILOS, for proximal humerus fracture type II and type III are satisfactory and encouraging in all age groups. Still there is scope to improve results in type IV fractures especially in elderly with osteoporotic bones.
Downloads
References
2. Kristiansen B, Barfod G, Bredesen J, et al. Epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 1987 Feb;58(1):75-7.[pubmed]
3. Iannotti J P, Ramsey M L, Williams G R, Warner J P. Non prosthetic management of proximal humeral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 2003; 85: 1578-93.
4.Paavolainen P, Björkenheim JM, Slätis P, Paukku P. Operative treatment of severe proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 1983 Jun;54(3):374-9.[pubmed]
5. Wijgman AJ, Roolker W, Patt TW, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of three and four-part fractures of the proximal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002 Nov;84-A(11):1919-25.[pubmed]
6. Resch H, Povacz P, Fröhlich R, Wambacher M. Percutaneous fixation of three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997 Mar;79(2):295-300.[pubmed]
7. Mittlmeier TW, Stedtfeld HW, Ewert A, et al. Stabilization of proximal humeral fractures with an angular and sliding stable antegrade locking nail (Targon PH). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 4:136-46.[pubmed]
8. Fankhauser F, Boldin C, Schippinger G, et al. A new locking plate for unstable fractures of the proximal humerus. Clin OrthopRelat Res. 2005 Jan;(430):176-81.[pubmed]
9. WannerGA ,Wanner-Schmid E, Romero J, et al. Internal fixation of displaced proximal humeral fractures with two one-third tubular plates. J Trauma. 2003 Mar;54(3):536-44. doi:10.1097/01.TA.0000052365.96538.42
10. Schmal H, Klemt C, Südkamp NP. [Evaluation of shoulder arthroplasty in treatment of four-fragment fractures of the proximalhumerus]. Unfallchirurg. 2004 Jul;107(7):575-82.doi:10.1007/s00113-004-0772-4.[pubmed]
11. Moonot P, Ashwood N, Hamlet M. Early results for treatment of three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus using the PHILOS plate system. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007 Sep;89(9):1206-9.doi:10.1302/0301-620X.89B9.18528.[pubmed]
12. Palvanen M, Kannus P, Niemi S, Parkkari J. Update in the epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Clin OrthopRelat Res. 2006 Jan;442:87-92.[pubmed]
13. Brunner F, Sommer C, Bahrs C, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using a proximal humerallocked plate: a prospective multicenter analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2009 Mar;23(3):163-72. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181920e5b.[pubmed]
14. Liu XW, Fu QG, Xu SG, Zhang CC, Su JC, WangPF, et al. Application of PHILOS plate with injectable artificial bone for the treatment ofproximal humeral fractures in elderly patients.ZhongguoGushang. 2010;23(3):180-2.
15. Rees J, Hicks J, Ribbans W. Assessment and management of three-and four-part proximal humeral fractures. Clin OrthopRelat Res. 1998 Aug;(353):18-29.[pubmed]
16. Kristiansen B, Christensen SW. Plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 1986 Aug;57(4):320-3.[pubmed]
17. Weinstein DM, Bratton DR, Ciccone WJ 2nd, Elias JJ. Locking plates improve torsional resistance in the stabilization of three-part proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006 Mar-Apr;15(2):239-43.doi:10.1016/j.jse.2005.08.006.[pubmed]
18. Walsh S, Reindl R, Harvey E, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a unique locking plate versus a standard plate for internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures in a cadaveric model. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006 Dec;21(10):1027-31. Epub 2006 Aug 17.doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2006.06.005
19. Zyto K. Non-operative treatment of comminuted fractures of the proximal humerus in elderly patients. Injury. 1998 Jun;29(5):349-52.[pubmed]
20. Arumugam S, Arumugam V, Raviraman V. Surgical management of proximal humerus fracture treated with locking compression plate. Int J Res Orthop2017;3:1165-9.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

