Early functional outcome of intercondylar humerus fractures fixed with precontoured dual plating in inverted Y-Fashion
Abstract
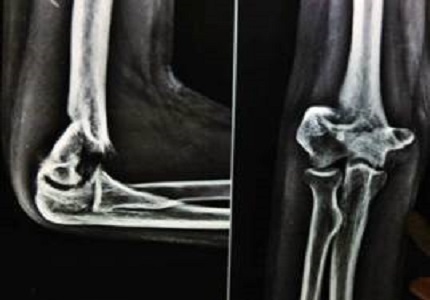
Objective: In this study we report the functional outcome of patients with intercondylar distal humerus fractures treated by precontoured angular stable anatomical locking plates in inverted Y fashion, using a standard approach.
Materials and Methods: A total number of 24 patients with AO type C closed intercondylar distal humerus fractures were operated with open reduction through an olecranon osteotomy approach and internal fixation using two plates in inverted-Y fashion. Patients were followed at 4 weeks, 6 weeks, 12 weeks and thereafter every 6 months. They were evaluated using the Mayo Elbow performance index and Riseborough and Radin Score.
Results: There were 9 (37.5%) men and 15 (62.5%) women with mean age of 46.72 years.79.17% of the cases were following fall and rest following Motor vehicle accident. AO type C2 fractures accounted for 45.83% of cases; type C3 fractures accounted for 33.33% of cases and type C1 accounted for 20.84%. According the Riseborough and Radin criteria, the results were Good in 14(58.33%) of patients, Fair in 9(37.50%) and Poor in 1(4.17%). According to MEPI, we had Excellent results in 5(20.83%), Good in 12(50%), Fair in 6(25%) and Poor in 1(4.17%) patients. The mean MEPI was 82±18.Thus according to MEPI, we achieved excellent to good results in ~70% of patients with 100% union rate and complications less than 13%.
Conclusion: Intercondylar fractures of humerus treated by Dual plating in inverted Y-fashionoffers a reliable and stable fixation permitting early mobilization and comparable functional outcome with good union rates.
Downloads
References
2. Morrey BFFractures of the distal humerus: role of elbow replacement. Orthop Clin North Am. 2000 Jan; 31(1):145-54. [PubMed]
3. Charissoux, J.L., Vergnenegre, G., Pelissier, M., et al.. Epidemiology of distal humerus fractures in the elderly. Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research. Volume 99, Issue 7, November 2013, Pages 765-769 DOI:10.1016/j.otsr.2013.08.002 (PMID: 24075780)
4. Robinson CM, Hill RM, Jacobs N, et al. Adult distal humeral metaphyseal fractures: epidemiology and results of treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 2003 Jan;17(1):38-47. [PubMed]
5. Galano GJ, Ahmad CS, Levine WN. Current treatment strategies for bicolumnar distal humerus fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010 Jan;18(1):20-30.
6. Palvanen M, Kannus P, Niemi S, Parkkari J. Secular trends in distal humeral fractures of elderly women: nationwide statistics in Finland between 1970 and 2007. DOI:10.1016/j.bone.2009.11.025.
7. Sheps D.M., Kyle kemp., Hilde brand Kevin. Population-based incidence of distal humeral fractures among adults in a Canadian urban center. Current Orthopaedic Practice 2011; 22(5):437-442 • September 2011.DOI: 10.1097/BCO.0b013e318229d0b5.
8. Riseborough EJ, Radin EL. Intercondylar T fractures of the humerus in the adult. A comparison of operative and non-operative treatment in twenty-nine cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969 Jan;51(1):130-41.
9. Longo UG, Franceschi F, Loppini M, et al. Maffulli N, Denaro V. Rating systems for evaluation of the elbow. DOI:10.1093/bmb/ldn023
10. O'Driscoll SW. Optimizing stability in distal humeral fracture fixation. 2005;14(1): S186-S194. DOI:10.1016/j.jse.2004.09.033. [PubMed]
11. Helfet DL, Hotchkiss RN. Internal fixation of the distal humerus: a biomechanical comparison of methods. J Orthop Trauma. 1990;4(3):260-4. [PubMed]
12. Keon-Cohen BT. Fractures at the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1966 Dec;48(8):1623-39. [PubMed]
13. Doornberg JN, van Duijn PJ, Linzel D, et al. Surgical treatment of intra-articular fractures of the distal part of the humerus. Functional outcome after twelve to thirty years. DOI:10.2106/JBJS.F.00369.
14. Arnander MW, Reeves A, MacLeod IA, et al. A biomechanical comparison of plate configuration in distal humerus fractures. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e31816edbce.
15. Jacobson SR1, Glisson RR, Urbaniak JR. Comparison of distal humerus fracture fixation: a biomechanical study. J South Orthop Assoc. 1997 Winter;6(4):241-9. [PubMed]
16. Kimball JP, Glowczewskie F, Wright TW. Intraosseous blood supply to the distal humerus. DOI:10.1016/j.jhsa.2007.02.019. [PubMed]
17. Korner J, Lill H, Muller LP. 2003. The LCP-concept in the operative treatment of distal humerus fractures—biological, biomechanical and surgical aspects. Int J Care Injured 34: S-B20–S-B30. PMID:14580983.
18. Schwartz A, Oka R, Odell T, Mahar A. Biomechanical comparison of two different periarticular plating systems for stabilization of complex distal humerus fractures. DOI:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2006.04.018.
19. Wong AS, Baratz ME. Elbow fractures: distal humerus. J Hand Surg Am. 2009 Jan;34(1):176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.10.023. [PubMed]
20. Rakesh Kumar Gupta, Vinay Gupta, Dickey Richard Marak. Locking plates in distal humerus fractures: study of 43Patients. Chinese Journal of Traumatology Volume 16, Issue 4, August 2013, Pages 207-211.https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-1275.2013.04.004.
21. Gupta R, Khanchandani P. Intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus in adults: a critical analysis of 55 cases.Injury. 2002 Jul;33(6):511-5.
22 Subramanian V, Rajanish R Menon, Kumaran CM. Functional outcome of supracondylar – inter condylar fractures of humerus in adults treated by Y plate fixation. Kerala Journal Of Orthopaedics Volume 27| Issue 1 | January 2014.
23. Amite Pankaj, G Mallinath, Rajesh Malhotra, et al., Surgical management of intercondylar fractures of the humerus using triceps reflecting anconeus pedicle (TRAP) approach. Indian journal of orthopaedics. Indian J Orthop. 2007 Jul-Sep; 41(3): 219–223. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.33686 PMID: 21139748.
24 Swagat Mahapatra, Vineet Thomas Abraham. Functional Results of Intercondylar Fractures of the Humerus Fixed with Dual Y-Plate; A Technical Note. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2017 Jan; 5(1): 36–41. PMID: 28246622
25. Lee SK, Kim KJ, Park KH, Choy WS. A comparison between orthogonal and parallel plating methods for distal humerus fractures: a prospective randomized trial DOI:10.1007/s00590-013-1286-y. [PubMed]
26. Lan X, Zhang LH, Tao S, et al. Zhang Q, Liang XD, Yuan BT, Xu WP, Yin P, Tang PF. Comparative study of perpendicular versus parallel double plating methods for type C distal humeral fractures. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013 Jun;126(12):2337-42.
27. Aslam N, Willett K. Functional outcome following internal fixation of intraarticular [13] fractures of the distal humerus (AO type C). Acta Orthop Belg. 2004;70(2):118- 22. [PubMed]
28. Tian D, Jing J, Qian J, et al., Comparison of two different double-plate fixation [14] methods with olecranon osteotomy for intercondylar fracture of distal humerus of young adults. Exp Ther Med. 2013; 6(1):147-151. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1102.
29. Leigey DF, Farrell DJ, Siska PA, Tarkin IS. Bicolumnar 90-90 plating of low-energy distal humeral fractures in the elderly patient. DOI:10.1177/2151458514526882
30. Rebuzzi E, Vascellari A, SchiavettiS.The use of parallel pre-contoured plates in the treatment of A and C fractures of the distal humerus. DOI:10.1007/s12306-009-0051-1
31 Sanjiv Kumar, Sudhir Singh, Dharmenderkumar, et al., Intercondylar Humerus Fracture- Parallel Plating and Its Results. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Jan; 9(1): RC01–RC04. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/12137.5479.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

