A study of Diagnosis and surgical management of pancreatic insulinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Insulinomas are the most common functioning neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas, occurring in almost 1-4 per 1 million persons each year. They pose a challenge for pre-operative localization. Many invasive and non-invasive methods exist for localization of an insulinoma. Intra-operative ultrasonography (IOUS) with palpation can be done for tumors not localized by conventional imaging modalities. Pancreas Preserving surgery is the treatment of choice. This article gives an overview on localization and surgical strategies for treatment of insulinoma.
Materials and Methods: This is a retrospective data of the patients undergoing surgical treatment of insulinoma in the Osmania General Hospital, Hyderabad between 2007 to 2017. Demographic data, symptoms and diagnostic tests and type of resections were analyzed from medical records. All patients had a complete intraoperative exploration of the pancreas done by digital palpation and intra operative ultrasonography.
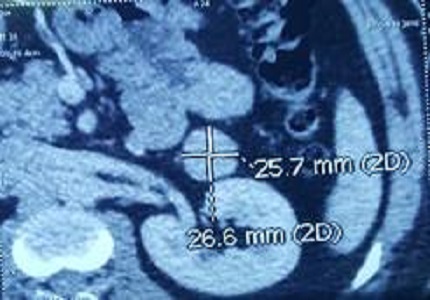
Results: 10 cases (6 males and 4 females) of insulinoma aged between 22 and 55 years, with a median age of 30 years were included in the analysis. The size of the insulinoma ranged between 1.2 to 3 cm with average size of 2.14cm. 8 patients presented with Neuro glycopenicsymptoms however sympatho adrenergic symptoms were present in all cases. Different modalities were employed for pre-operative localization of these patients out of which 5 cases were localized with CT, 2 cases with MRI, 1 case with EUS, 2 of them could not be localized preoperatively were localized by IOUS. Tumor was in Head 2 cases, in the neck1 case and in the body/ Tail in 7 cases. 2 patients underwent Enucleation, 5 underwent distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy, 2 under went distal pancreatectomy and 1 underwent central pancreatectomy. 4 had pancreatic leak. All are symptom free and no episode of hypoglycemia at the time of discharge.
Conclusion: Insulinomas are the most common neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas. Surgical resection is the treatment of choice for insulinomas. From a surgical stand point, localization of the tumor is of critical importance. Intraoperative Ultrasonography with palpation gives good help in localizing the lesion.
Downloads
References
2. Grant CS. InsulinomaBest Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2005 Oct;19(5):783-98. [PubMed]
3. Service FJ, McMahon MM, O'Brien PC, Ballard DJ. Functioninginsulinoma--incidence, recurrence, and long-term survival of patients: a 60-year study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1991 Jul;66(7):711-9.
4. Tucker ON, Crotty PL, Conlon KC.The management of insulinoma.Br J Surg. 2006 Mar;93(3):264-75.
5. Mathur A, Gorden P, Libutti SK. Insulinoma.SurgClin North Am. 2009 Oct;89(5):1105-21. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2009.06.009. [PubMed]
6. Ravi K, Britton BJ. Surgical approach to insulinomas: are pre-operative localisation tests necessary?Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2007 Apr;89(3):212-7. [PubMed]
7. Vinik AI, Delbridge L, Moattari R, Cho K, Thompson N. Transhepatic portal vein catheterization for localization of insulinomas: a ten-year experience. Surgery.1991 Jan;109(1):1-11; discussion 111. [PubMed]
8. Wiesli P, Brändle M, Schmid C, Krähenbühl L, Furrer J, Keller U, Spinas GA, Pfammatter T. Selective arterial calcium stimulation and hepatic venous sampling in the evaluation of hyperinsulinemichypoglycemia: potential and limitations.J VascIntervRadiol. 2004 Nov;15(11):1251-6. [PubMed]
9. Anderson MA, Carpenter S, Thompson NW, Nostrant TT, Elta GH, Scheiman JM. Endoscopic ultrasound is highly accurate and directs management in patients with
neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas.Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Sep;95(9):2271-7. [PubMed]
10. Chung JC, Choi SH, Jo SH, Heo JS, Choi DW, Kim YI. Localization and surgical treatment of the pancreatic insulinomas.ANZ J Surg. 2006 Dec;76(12):1051-5. [PubMed]
11. Chatziioannou A, Kehagias D, Mourikis D, Antoniou A, Limouris G, Kaponis A, Kavatzas N, Tseleni S, Vlachos L. Imaging and localization of pancreatic insulinomas.Clin Imaging. 2001 Jul-Aug;25(4):275-83.
12. Sheth S, Hruban RK, Fishman EK. Helical CT of islet cell tumors of the pancreas: typical and atypical manifestations.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002 Sep;179(3):725-30. [PubMed]
13. Noone TC, Hosey J, Firat Z, Semelka RC. Imaging and localization of islet-cell tumours of the pancreas on CT and MRI.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Jun;19(2):195-211. [PubMed]
14. Owen NJ,Sohaib SA, Peppercorn PD, Monson JP, Grossman AB, Besser GM, Reznek RH. MRI of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours.Br J Radiol. 2001 Oct;74(886):968-73.
15. Thoeni RF, Mueller-Lisse UG, Chan R, Do NK, Shyn PB. Detection of small, functional islet cell tumors in the pancreas: selection of MR imaging sequences for optimal sensitivity.Radiology. 2000 Feb;214(2):483-90. [PubMed]
16. Anaye A, Mathieu A, Closset J, Bali MA, Metens T, Matos C. Successful preoperative localization of a small pancreatic insulinoma by diffusion-weighted MRI.JOP. 2009 Sep 4;10(5):528-31.
17. Kann PH, Ivan D, Pfützner A, Forst T, Langer P, Schaefer S. Preoperativediagnosis of insulinoma: low body mass index, young age, and female gender areassociated with negative imaging by endoscopic ultrasound. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007Aug;157(2):209-13.
18. McLean AM, Fairclough PD. Endoscopic ultrasound in the localisation ofpancreatic islet cell tumours. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005Jun;19(2):177-93. Review.
19. Kann PH, Rothmund M, Zielke A. Endoscopic ultrasound imaging of insulinomas:limitations and clinical relevance. ExpClin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2005Sep;113(8):471-4. [PubMed]
20. Tseng LM, Chen JY, Won JG, Tseng HS, Yang AH, Wang SE, Lee CH. The role of intra-arterial calcium stimulation test with hepatic venous sampling (IACS) inthe management of occult insulinomas. Ann SurgOncol. 2007 Jul;14(7):2121-7. Epub2007 Apr 12. [PubMed]
30. Morera J, Guillaume A, Courtheoux P, Palazzo L, Rod A, Joubert M, Reznik Y. Preoperative localization of an insulinoma: selective arterial calcium stimulation test performance.J Endocrinol Invest. 2016 Apr;39(4):455-63. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0406-4. Epub 2015 Nov 17.
31. Guettier JM, Kam A, Chang R, Skarulis MC, Cochran C, Alexander HR, Libutti SK, Pingpank JF, Gorden P.Localization of insulinomas to regions of the pancreas by intraarterial calcium stimulation: the NIH experience.J Clin EndocrinolMetab.2009 Apr;94(4):1074-80. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1986. Epub2009Feb3. [PubMed]
23. Chung JC, Choi SH, Jo SH, Heo JS, Choi DW, Kim YI. Localization and surgical treatment of the pancreatic insulinomas. ANZ J Surg. 2006 Dec;76(12):1051-5.
24. Jackson JE. Angiography and arterial stimulation venous sampling in the localization of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Jun;19(2):229-39. [PubMed]
25. Gimm O, König E, Thanh PN, Brauckhoff M, Karges W, Dralle H. Intra-operative quick insulin assay to confirm complete resection of insulinomas guided byselective arterial calcium injection (SACI). Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2007Nov;392(6):679-84. Epub 2007 Feb 9.
26. Tseng HC, Yao CZ, Zhong SX, Zhang JX, Zhu Y. Percutaneous transhepatic portal vein catheterization for localization of insulinoma. World J Surg. 1984Aug;8(4):575-82. [PubMed]
27. Kaczirek K, Ba-Ssalamah A, Schima W, Niederle B. The importance ofpreoperative localisation procedures in organic hyperinsulinism--experience in 67patients. Wien KlinWochenschr. 2004 Jun 30;116(11-12):373-8. PubMed PMID:15291289.
28. Gritzmann N, Macheiner P, Hollerweger A, Hübner E. CT in the differentiation of pancreatic neoplasms--progress report. Dig Dis. 2004;22(1):6-17.
29. Akerström G, Hellman P, Hessman O, Osmak L. Surgical treatment of endocrine pancreatic tumours. Neuroendocrinology. 2004;80 Suppl 1:62-6. [PubMed]
30. de Herder WW. Insulinoma.Neuroendocrinology. 2004;80 Suppl 1:20-2. [PubMed]
31. Vázquez Quintana E. The surgical management of insulinoma.BolAsoc Med P R. 2004 Jan-Feb;96(1):33-8. [PubMed]
32. Lairmore TC, Moley JF. Endocrine pancreatic tumors. Scand J Surg.2004;93(4):311-5. Review. PubMed PMID: 15658673.
33. Jyotsna VP, Rangel N, Pal S, Seith A, Sahni P, Ammini AC. Insulinoma:Diagnosis and surgical treatment. Retrospective analysis of 31 cases. Indian JGastroenterol. 2006 Sep-Oct;25(5):244-7.
34. Kaczirek K, Ba-Ssalamah A, Schima W, Niederle B. The importance ofpreoperative localisation procedures in organic hyperinsulinism--experience in 67patients. Wien KlinWochenschr. 2004 Jun 30;116(11-12):373-8.
35. Jensen RT, Cadiot G, Brandi ML, de Herder WW, Kaltsas G, Komminoth P, Scoazec JY, Salazar R, Sauvanet A, Kianmanesh R; Barcelona Consensus Conferenceparticipants. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the management of patients withdigestive neuroendocrine neoplasms: functional pancreatic endocrine tumorsyndromes. Neuroendocrinology. 2012;95(2):98-119. doi: 10.1159/000335591. Epub2012 Feb 15.
36. Kulke MH, Anthony LB, Bushnell DL, de Herder WW, Goldsmith SJ, Klimstra DS, Marx SJ, Pasieka JL, Pommier RF, Yao JC, Jensen RT; North American NeuroendocrineTumor Society (NANETS). NANETS treatment guidelines: well-differentiatedneuroendocrine tumors of the stomach and pancreas. Pancreas. 2010Aug;39(6):735-52. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181ebb168.
37. Crippa S, Zerbi A, Boninsegna L, Capitanio V, Partelli S, Balzano G, Pederzoli P, Di Carlo V, Falconi M. Surgical management of insulinomas: short- andlong-term outcomes after enucleations and pancreatic resections. Arch Surg. 2012 Mar;147(3):261-6. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2011.1843.
38. Laje P, Stanley CA, Palladino AA, Becker SA, Adzick NS. Pancreatic headresection and Roux-en-Y pancreaticojejunostomy for the treatment of the focalform of congenital hyperinsulinism. J Pediatr Surg. 2012 Jan;47(1):130-5. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.10.032. [PubMed]
39. Shoup M, Brennan MF, McWhite K, Leung DH, Klimstra D, Conlon KC. The value of splenic preservation with distal pancreatectomy.Arch Surg. 2002 Feb;137(2):164-8. [PubMed]
40. Mabrut JY, Fernandez-Cruz L, Azagra JS, Bassi C, Delvaux G, Weerts J, Fabre JM, Boulez J, Baulieux J, Peix JL, Gigot JF; Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Section(HBPS) of the Royal Belgian Society of Surgery; Belgian Group for EndoscopicSurgery (BGES); Club Coelio. Laparoscopic pancreatic resection: results of amulticenter European study of 127 patients. Surgery. 2005 Jun;137(6):597-605. [PubMed]
41. Goletti O, Celona G, Monzani F, Caraccio N, Zocco G, Lippolis PV, BattiniA,Seccia M, Cavina E. Laparoscopic treatment of pancreatic insulinoma. Surg Endosc.2003 Sep;17(9):1499. Epub 2003 Jun 17. PubMed PMID: 12802660.
42. Jaroszewski DE, Schlinkert RT, Thompson GB, Schlinkert DK. Laparoscopic localization and resection of insulinomas.Arch Surg. 2004 Mar;139(3):270-4. [PubMed]
43. Roland CL, Lo CY, Miller BS, Holt S, Nwariaku FE. Surgical approach andperioperative complications determine short-term outcomes in patients withinsulinoma: results of a bi-institutional study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008Dec;15(12):3532-7. doi: 10.1245/s10434-008-0157-y. Epub 2008 Sep 30.
44. Jürgensen C, Schuppan D, Neser F, Ernstberger J, Junghans U, Stölzel U. EUS-guided alcohol ablation of an insulinoma.GastrointestEndosc. 2006 Jun;63(7):1059-62. [PubMed]
45. Limmer S, Huppert PE, Juette V, Lenhart A, Welte M, Wietholtz H. Radiofrequency ablation of solitary pancreatic insulinoma in a patient with episodes of severe hypoglycemia.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Sep;21(9):1097-101. [PubMed]
46. Moore TJ, Peterson LM, Harrington DP, Smith RJ. Successful arterial embolization of an insulinoma.JAMA. 1982 Sep 17;248(11):1353-5.
47. Uflacker R. Arterial embolization as definitive treatment for benigninsulinoma of the pancreas. J VascIntervRadiol. 1992 Nov;3(4):639-44;discussion 644-6. [PubMed]
48. Vezzosi D, Bennet A, Courbon F, Caron P. Short- and long-term somatostatin analogue treatment in patients with hypoglycaemia related to endogenoushyperinsulinism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008 Jun;68(6):904-11.Epub 2007 Nov 19.
49. Kishikawa H, Okada Y, Hirose A, Tanikawa T, Kanda K, Tanaka Y. Successful treatment of insulinoma by a single daily dose of octreotide in two elderlyfemale patients. Endocr J. 2006 Feb;53(1):79-85. [PubMed]
50. Katabami T, Kato H, Shirai N, Naito S, Saito N. Successful long-term treatment with once-daily injection of low-dose octreotide in an aged patient with insulinoma.Endocr J. 2005 Oct;52(5):629-34. [PubMed]
51. Bonato FT, Coelho JC, Petruzzielo A, Matias JE, Ferreira GA. Surgical treatment of pancreatic insulinomas.Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2012 Apr-Jun;25(2):101-4.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

