A comparative study between plating & intramedullary nailing for displaced diaphyseal fractures of radius and ulna in adults
Abstract
Background: In the current era of industrialization and with mechanized farming in India, fractures of forearm bones have become more common. The forearm serves an important role in the functioning of the upper extremity. Hence aggressive management through good anatomical reduction and internal fixation of these fractures has become a necessity. The purpose of this study was to assess and compare functional results of plating and nailing in fracture stabilization.
Methods: Retrospective and prospective study with the sample size of 20 patients with both bone forearm fractures. 10 patients were treated with dynamic compression plating and remaining 10 with intramedullary square nails. Results were assessed by time for union, type of fractures, range of motion of elbow and wrist joint, complications and functional assessment were done by Grace- Eversmann Criteria and DASH questionnaire. Results were statistically analysed with Mann- Whitney U-test.
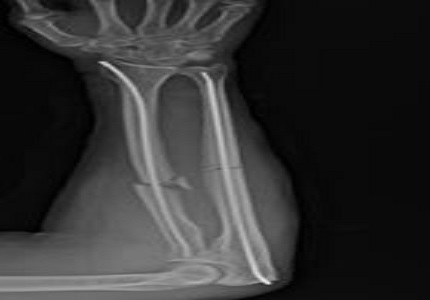
Results: Out of 20 cases 18 were males and 2 females, with average age of 38.5 years. 12 fractures were of A32 type according to AO classification. Good or full range of mobility of elbow and wrist joints with excellent & satisfactory results were present in 16 patients as per Grace-Eversmann criteria. 2 patients showed ulnar nail back out while other 2 had delayed union of fracture, all seen with intramedullary nailing.
Conclusion: There was no statistically significant difference between results of nailing and plating. However, it is concluded that while good functional results can be obtained with intramedullary nailing of forearm fractures, open reduction and internal fixation offracture remains the treatment of choice for most forearm fractures with adherence to AO principles.
Downloads
References
2. Bengnér U, Johnell O. Increasing incidence of forearm fractures. A comparison of epidemiologic patterns 25 years apart. Acta Orthop Scand. 1985 Apr;56(2):158-60. [PubMed]
3. Alffram Pa, Bauer GC. Epidemiology of fractures of the forearm. A biomechanical investigation of bone strength.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962 Jan;44-A:105-14. [PubMed]
4. Schmitt KU, Zürich PF, Muser MH, Walz F. Trauma Biomechanics: Accidental injury in traffic and sports. Springer Science & Business Media, 2009.
5. KB Ravi, TS Raghavendra, S Balasubramanian, Forearm Bone fractures: Dynamic Compression Platting Vs Locking compression plating – Randomised control study. Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; June 2014: Vol.-3, Issue- 3, P. 226-232.
6. Goldfarb CA, Ricci WM, Tull F, Ray D, Borrelli J Jr. Functional outcome after fracture of both bones of the forearm.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005 Mar;87(3):374-9.
7. Rao MR, Kader E, Sujith SV, Thomas V. Nail-plate combination in management of fracture both bone forearm. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2002: 84(B):252-253).
8. Rao R. A prospective study of pediatric forearm bone fractures treated with closed intramedullary square nailing. J. Orthopaedics. 2009;6(1):12–12.
9. Grace TG, Eversmann WW Jr. Forearm fractures: treatment by rigid fixation with early motion.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980 Apr;62(3):433-8. [PubMed]
10. Gummesson C, Atroshi I, Ekdahl C. The disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) outcome questionnaire: longitudinal construct validity and measuring self-rated health change after surgery. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2003 Jun 16;4(1):11. [PubMed]
11. McKnight PE, Najab J. Mann-Whitney U Test. CorsiniEncyclopedia of Psychology. 2010.DOI: 10.1002/9780470479216.corpsy0524.
12. Thompson JE. Anatomical methods of approach in operations on the long bones of the extremities. Annals of surgery. 1918 Sep;68(3):309. [PubMed]
13. Henry MH, Griggs SM, Levaro F, Clifton J, Masson MV. Volar approach to dorsal displaced fractures of the distal radius. Techniques in hand & upper extremity surgery. 2001 Mar 1;5(1):31-41.
14. Anderson LD, Sisk D, Tooms RE, Park WI 3rd.Compression-plate fixation in acute diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975 Apr;57(3):287-97.
15. Sage, F.P. Medullary fixation of fractures of the forearm. A study of the medullary canal of the radius and a report of 50 fractures of the radius treated with a prebent triangular nail. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959 December;41:1489–1516.
16. Crenshaw AH, Zinar DM, Pickering RM. Intramedullary nailing of forearm fractures.Instr Course Lect. 2002;51:279-89.
17. Gadegone W, Salphale YS, Lokhande V.Screw elastic intramedullary nail for the management of adult forearm fractures.Indian J Orthop.2012 Jan;46(1):65-70. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.91637.
18. Schone G. Zurbehandulung von vorderarmfrakturenmitbolzung. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1913;60: 2327-8.
19. VomSaal F. (1954): quoted by Marek F. M. 1961.
20. Lee YH, Lee SK, Chung MS, Baek GH, Gong HS, Kim KH.Interlocking contoured intramedullary nail fixation for selected diaphyseal fractures of the forearm in adults.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Sep;90(9):1891-8. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.G.01636. [PubMed]
21. Amit Y, Salai M, Chechik A, Blankstein A, Horoszowski H. Closing intramedullary nailing for the treatment of diaphyseal forearm fractures in adolescence: a preliminary report. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 1985;5(2):143.
22. Al-Sadek TA, Niklev D, Al-Sadek A. Diaphyseal Fractures of the Forearm in Adults, Plating Or Intramedullary Nailing Is a Better Option for the Treatment?. Open access Macedonian journal of medical sciences.2016 Dec 15;4(4):670. http://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2016.138.
23. Müller ME, Allgöwer M, Perren SM. Manual of internal fixation: techniques recommended by the AO-ASIF group. Springer Science & Business Media, 1991. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-02695- 3.
24. Vander Griend R, Tomasin J, Ward EF.Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral shaft fractures. Results using AO plating techniques.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986 Mar;68(3):430-3. [PubMed]
25. Arora R, Lutz M, Hennerbichler A, Krappinger D, Espen D, Gabl M.Complications following internal fixation of unstable distal radius fracture with a palmar locking-plate.J Orthop Trauma. 2007 May;21(5):316-22. [PubMed]
26. Deluca PA, Lindsey RW, Ruwe PA. Refracture of bones of the forearm after the removal of compression plates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988;70(9):1372-6. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623- 198870090-00015 PMid:3182889.
27. Khateeb MK, Akbar MN. Comparison of Intramedullary Nailing to Plating for Both-bone Forearm Fractures in Adult. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics Surgery. 2017;3(2):135-42. DOI : 10.18231/2395-1362.2017.0027


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

