A three year experience in Laparoscopic Appendectomy
Abstract
Background: Acute appendicitis is one of the most common causes of acute abdomen. It may occur from the time of infancy to old age, but the peak age of incidence is in the second and third decades of life. The lifetime risk of appendicitis is approximately 7-8%. Today in developed countries, about 8% of the population is treated for acute appendicitis in the course of their lifetime. The outcome can be very serious at both extremes of life and there is a life time risk of developing acute appendicitis in about 5-8%. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical results of laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) for the treatment of acute appendicitis.
Material and Methods: A retrospectiveanalysis fallpatients who underwent laparoscopic appendectomy diagnosed with acute appendicitis overa3-yearperiodwasreviewed. Data were retrieved from our departmental data base and analyzed using descriptive statistics. Most of the patients were diagnosed to have appendicitis by ultrasound or have ruled out other cause of right lower abdominal pain especially in females.
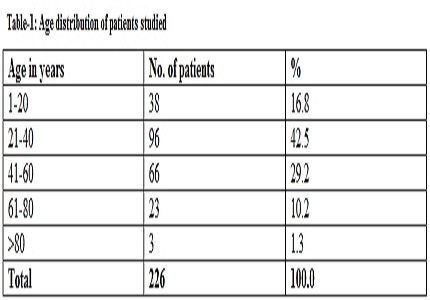
Results: Out of the 226 patients who underwent laparoscopic appendectomy, 138(61.1%) were females and the remaining 88(38.9%) were males. Most of them are in the age group of 21-40years. 171 (75.7%) patients were discharged within 48 hours.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic appendectomy is as safe and effective as conventional surgery, has a higher diagnostic yield, causes less trauma, and offers a more rapid postoperative recovery. Such features make laparoscopy a challenging alternative to laparotomy in premenopausal women referred for urgent abdominal or pelvic surgery, or both.
Downloads
References
2. Garbutt JM, Soper NJ, Shannon WD, Botero A, Littenberg B. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trialscomparing laparoscopic and open appendectomy. SurgLaparoscEndosc. 1999 Jan;9(1):17-26.
3. Golub R, Siddiqui F, Pohl D. Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy: a metaanalysis. J Am Coll Surg. 1998 May;186(5):545-53. [PubMed]
4. Andersson RE, Hugander A, Thulin AJ. Diagnostic accuracy and perforation rate in appendicitis: association with age and sex of the patient and with appendicectomy rate. Eur J Surg. 1992 Jan;158(1):37-41. [PubMed]
5. Katkhouda N, Friedlander MH, Grant SW, Achanta KK, Essani R, Paik P, Velmahos G, Campos G, Mason R, Mavor E. Intraabdominal abscess rate after laparoscopic appendectomy. Am J Surg. 2000 Dec;180(6):456-9; discussion 460-1. [PubMed]
6. So JB, Chiong EC, Chiong E, Cheah WK, Loman¬to D, Goh P, Kum CK. Laparoscopic appendec¬tomy for perforated appendicitis. December 2002, Volume 26, Issue 12, pp 1485–1488.
7. Chung RS, Rowland DY, Li P, Diaz J. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of laparoscopic versus conventional appendectomy. Am J Surg. 1999 Mar;177(3):250-6.
8. Nguyen DB, Silen W, Hodin RA. Appendectomy in the pre- and postlaparoscopic eras. J Gastrointest Surg. 1999 Jan-Feb;3(1):67-73.
9. Heinzelmann M, Schob O, Gianom D, Platz A, Simmen HP. Role of laparoscopy in the management of acute appendicitis. ZetralblChir. 1999; 124(12):1130-1136.
10. Shaikh AR, Sangrasi AK, Shaikh GA. Clinicaloutcomes of laparoscopic versus open appendectomy. JSLS. 2009 Oct-Dec;13(4):574-80.doi: 10.4293/108680809X1258998404524.
11. Peters JH, Ellison EC, Innes JT, Liss JL, Nichols KE, LomanoJM,etal.Safetyandefficacyoflaparoscopiccholecystectomy. A prospective analysis of 100 initial patients. Ann Surg 1991; 213:3-12.
12. Schirmer BD, Edge SB, Dix J, Hyser MJ, Hanks JB, Jones RS. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Treatment of choice for symptomaticcholelithiasis. Ann Surg. 1991 Jun;213(6):665-76; discussion 677.
13. Sauerland S, Lefering R, Holthausen U, Neugebauer EA. Laparoscopicvsconventionalappendectomy--a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. LangenbecksArch Surg. 1998 Aug;383(3-4):289-95.
14. Frazee RC, Roberts JW, Symmonds RE, Snyder SK, Hendricks JC, Smith RW, et al. A prospective randomized trial comparing open versus laparoscopic appendectomy. Ann Surg1994; 219:725-8.
15. Rashid A, Nazir S, Kakroo SM, Chalkoo MA, Razvi SA, Wani AA. Laparoscopicintervalappendectomyversusopenintervalappendectomy: a prospectiverandomized controlled trial. SurgLaparoscEndoscPercutan Tech. 2013 Feb;23(1):93-6. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e318277df6a.
16. Tata MD, Singh R, Bakar AA, Selvindoss P, P K, Gurunathan R. Laparoscopicappendicectomy: the idealprocedure for laparoscopicskilltraining for surgicalregistrars.Asian J Surg. 2008 Apr;31(2):55-8. [PubMed]
17. Duff SE, Dixon AR: Laparoscopic appendicectomy: safe and useful for training. Ann R Coll SurgEngl; 2000; 82(6):388-91.
18. Lau WY, Fan ST, Yiu TF, Chu KW, Suen HC, Wong KK. The clinicalsignificance of routinehistopathologicstudy of the resectedappendix and safety of appendicealinversion. SurgGynecolObstet. 1986 Mar;162(3):256-8. [PubMed]
19. Cuschieri A. Cost efficacy of laparoscopicvsopensurgery. Hospitals vs community. SurgEndosc. 1998 Oct;12(10):1197-8. [PubMed]


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

