An epidemiological study to calculate angle between transepicondylar axis and posterior condylar axis of distal femur on MRI in Indian population
Abstract
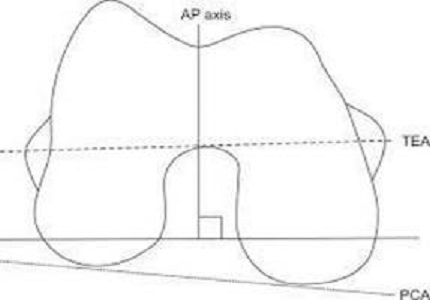
Introduction: Rotational positioning of femoral component is a critical aspect of total knee arthroplasty and evaluation of the landmark for rotation of distal femur is a challenge. Most Orthopaedic Surgeons prefer to use more available posterior femoral condyle axis.
Objectives: Aim of this study is to calculate the angle between TEA and PCA of distal femur on MRI in Indian population. This study is focused on the fact that angle between TEA and PCA may vary from 3 degrees and not fixed as most of the surgeons consider and most of the TKA implants are designed considering it fixed 3 degrees which can seriously affect the outcome and longevity of TKA.
Method: In this study MRI KNEE of 152 patients were studied to calculate angle between TEA AND PCA of distal femur. Software called LEONARDO wasutilized to calculate the angle on MRI images.
Results: Study shows the average angle of 4.54 degrees. No gender related disparity noted. No age-related increase or decrease of angle noted. In our study we found that, minimum angle between TEA and PCA is 2 degrees while maximum angle is 7.1 degrees.
Conclusion: Based on our study and results we conclude that the average angle between TEA and PCA in Indian population is 4.54 degrees. Thus, further studies will be required to investigate the effect of this angle over rotational alignment of femoral component during TKA’s and its immediate and longtermoutcomes. Study proves the angle not fixed to 3 degrees and individualistic approach from case to case basis maybe beneficial.
Downloads
References
2. AgliettiP,sensiL,Cuomo,Ciardullo.Rotational position of femoral and tibial component in TKA using the femoral transepicondylaraxis .clinOrthopRelat Res.2008;466(11):2751-275. [PubMed]
3. Rossi R,Bruzzone,Bonasia,MarmottA,Castoldi.Evaluation of tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty:a cadaver study.KneeSurg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2010;18(7)889-893.
4. Zhang XL, Zhang W, Shao JJ. Rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty;non image based navigation system versus conventional technique.Chin Med J.(Engl).2012; 25(2):236-243. [PubMed]
5. SunT,LvH,Hong.Rotational landmarks and total knee arthroplasty in osteoarthritis knees ZhongguoXiu fu.2007;21(3):226-230. [PubMed]
6. UeharaK,KadoyaY,KobayashiA,OhashiH,YamanoY.Boneanatomyandrotatonal alignment total knee arthroplasty.ClinOrthopRelatRes.2002 ;402:196-201.
7. Berhouet J, Beaufils P, Boisrenoult P, FrascaD,PujolN.Rotatinal positioning of the tibial tray in total knee arthroplasty; a CT evaluation OrthopRelat Res. 2011;97(7): 699-704.
8. Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS.Determining the rotational alignment of femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using epicondylar axis,.ClinOrthopRelat Res.1993;286:40-47.
9. Olcott CW, Scott RD. A comparison of 4 intraoperative methods to determine femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2000;15(1):22-6.
10. Insall JN, Scuderi GR, Komistek RD, Math K, Dennis DA, Anderson DT. Correlation between condylar lift-off and femoral component alignment. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 2002;(403):143-52 11. J. [PubMed]
11. Jerosch J, Peuker E, Philipps B, Filler T. Interindividual re- producibility in perioperative rotational alignment of femo- ral components in knee prosthetic surgery using the tran- sepicondylar axis. Knee Surg Sports TraumatolArthrosc. 2002;10(3):194-7.
12. Kinzel V, Ledger M, Shakespeare D. Can the epicondylar axis be defined accurately in total knee arthroplasty? Knee.2005;12(4):293-6.
13. Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM. How precise is the determination of rotational alignment of the femoral prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty: an in vivo study. J Arthroplasty.2007;22(7):1042-8. [PubMed]
14. Siston RA, Patel JJ, Goodman SB, Delp SL, Giori NJ. The variability of femoral rotational alignment in total knee ar- throplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(10):2276-80.
15. Benjamin J. Determining femoral component position us- ing CAS and measured resection. ClinOrthopRelat Res.2008;466(11):2745-50.
16. Alifidi RJ, Haaga JR. El Yousef SJ, et a!. Preliminary experimental results in humans and animals with a superconducting, wholebody. nuclear magnetic resonance scanner. Radiology 1982; 143: 17581.
17. Akagi M, Matsusue Y, Mata T, et al. Effect of rotational alignment on patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. ClinOrthop1999;366:155-63. [PubMed]
18. Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. ClinOrthop1998;356:14&53.
19. Griffin FM. Insall JN, Scuderi GR. The posterior condylar angle in osteoarthritic knees. J Arthroplasty1988;12:812-5.
20. Katz MA, Beck TD, Silber JS, et al. Determining femoral rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty: reliability of techniques. J Arthroplasty2001;16:30145. [PubMed]
21. Poilvache PL, Insall JN, Scuderi GR, Font-Rodriguez DE. Rotational landmarks and sizing of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty. ClinOrthop1996;331:3546.
22. Gujarathi N, Putti AB, Abboud RJ, MacLean JG, Espley AJ, Kellett CF. Risk of periprosthetic fracture after anterior femoral notching. Acta Orthop. 2009;80:553–556.
23. Mont MA, Urquhart MA, Hungerford DS, Krackow KA. Intra- medullary goniometer can improve alignment in knee arthroplasty surgery. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12:332–336.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

