Comparison of outcomes of supracondylar femur fractures treated with locking compression plate vs supracondylar nail
Keywords:
Supracondylar femur fractures, LCP, SCN, Schatzker and Lambert criteria
Abstract
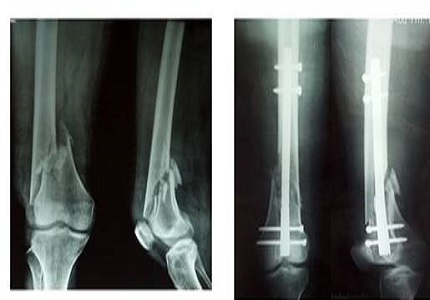
Objective: To compare the outcomes of supracondylar femur (SC) fractures treated with locking compression plate (LCP) with supracondylar nail (SCN).
Methods: Analysis of 90 cases was done out of which 45 were treated with supracondylar nail and 45 with LCP.
Results: Results were graded according to Schatzker and Lambert criteria. In LCP group 28 (62.22%) had excellent, 12 (26.66%) had good, 2 (4.44%) had Fair and 3 (6.66%) had poor results while in SCN group 22 had excellent (48.88%), 9 had good (20%), 6 had fair (13.33%) and 8 had poor (17.77%) results.
Conclusion: Locking condylar plate group had the best functional result followed by SCN group according to Schatzker and Lambert criteria.
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
References
1. Kolmert L, Wulff K. Epidemiology and treatment of distal femoral fractures in adults. Acta Orthop Scand. 1982 Dec;53 (6):957-62. [PubMed]
2. Martinet O, Cordey J, Harder Y, Maier A, Bühler M, Barraud GE. The epidemiology of fractures of the distal femur. Injury. 2000 Sep;31 Suppl 3:C62-3. [PubMed]
3. Arneson TJ, Melton LJ 3rd, Lewallen DG, O'Fallon WM. Epidemiology of diaphyseal and distal femoral fractures in Rochester, Minnesota, 1965-1984. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 1988 Sep;(234):188-94. [PubMed]
4. Kretttek C, Schandelmeier P, Tscherne H. Distal femoral fractures. Unfallchirurg. 1996; 90:2. [PubMed]
5. Albert MJ.SupracondylarFractures of the Femur. J Am AcadOrthop Surg.1997 May;5(3):163-171. [PubMed]
6. Ruedi T, Murphy WM (2000) AO Principles of Fracture Management. Vol. 1. Thieme: Stuttgart-New York. [PubMed]
7. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 1979 Jan-Feb;(138):77-83.
8. Smith WR, Ziran BH, Anglen JO, Stahel PF.Lockingplates: tips and tricks.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2007 Oct;89(10):2298-307. [PubMed]
9. Zlowodzki M, Williamson S, Cole PA, Zardiackas LD, Kregor PJ.Biomechanicalevaluation of the lessinvasivestabilization system, angledbladeplate, and retrogradeintramedullarynail for the internal fixation of distalfemur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004 Sep;18(8):494-502. [PubMed]
10. Roos EM, Roos HP, Lohmander LS, Ekdahl C, Beynnon BD. Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) and HSS—development of a self-administered outcome measure Orthop Sports Phys Ther 1998;2888-96.
11. Zlowodzki M, Bhandari M, Marek DJ, Cole PA, Kregor PJ. Operativetreatment of acutedistalfemur fractures: systematic review of 2 comparative studies and 45 case series (1989 to 2005). J Orthop Trauma. 2006 May;20 (5):366-71. [PubMed]
12. Carmack DB, Berton RM, Kingston C, Zmurko M, Watson JT, Richardson M. Identification of the optimal intercondylar starting point for retrograde femoral nailing: an anatomic study. J Trauma. 2003 Oct;55(4):692-5.
13. Gellman RE, Paiement GD, Green HD, Coughlin RR. Treatment of supracondylar femoral fractures with a retrograde intramedullary nail. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 1996 Nov;(332):90-7. [PubMed]
14. Watanabe Y, Takai S, Yamashita F, Kusakabe T, Kim W, Hirasawa Y. Second-generation intramedullary supracondylar nail for distal femoral fractures. IntOrthop. 2002;26(2):85-8.
15. Lucas. Quoted by Rockwood CA, Green DP. Fractures in adult,45h ed,Vol.II, pg.1972-93,1996.
16. Schatzker J, Horne G, Waddell J.TheTorontoexperiencewithsupracondylarfracturesoffemur.Injury 6,pg.113-28,1975. [PubMed]
17. Markmiller M, Konrad G, Südkamp N. Femur-LISS and distal femoral nail for fixation of distal femoral fractures: are there differences in outcome and complications? ClinOrthopRelat Res. 2004 Sep;(426):252-7. [PubMed]
18. Henderson CE, Lujan TJ, Kuhl LL, Bottlang M, Fitzpatrick DC, Marsh JL. 2010 mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: healing complications
are common after lockedplating for distal femur fractures. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 2011 Jun;469(6):1757-65. doi: 10.1007/s11999-011-1870-6. Epub 2011 Mar 22. [PubMed]
19. Weight M, Collinge C. Early results of the less invasive stabilization system for mechanically unstable fractures of the distalfemur (AO/OTA types A2, A3, C2, and C3). JOrthop Trauma. 2004 Sep;18(8):503-8. [PubMed]
20. Kregor PJ, Stannard JA, Zlowodzki M, Cole PA. Treatment of distal femur fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 103 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004 Sep;18(8):509-20. [PubMed]
21. Schandelmaier P, Partenheimer A, Koenemann B, Grün OA, Krettek C. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury. 2001 Dec;32 Suppl 3:SC55-63. [PubMed]
22. Schütz M, Müller M, Krettek C, Höntzsch D, Regazzoni P, Ganz R, Haas N. Minimally invasive fracture stabilization of distalfemoral fractures with the LISS: a prospective multicenter study. Results of a clinical study with special emphasis on difficult cases. Injury. 2001 Dec;32 Suppl 3:SC48-54. [PubMed]
2. Martinet O, Cordey J, Harder Y, Maier A, Bühler M, Barraud GE. The epidemiology of fractures of the distal femur. Injury. 2000 Sep;31 Suppl 3:C62-3. [PubMed]
3. Arneson TJ, Melton LJ 3rd, Lewallen DG, O'Fallon WM. Epidemiology of diaphyseal and distal femoral fractures in Rochester, Minnesota, 1965-1984. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 1988 Sep;(234):188-94. [PubMed]
4. Kretttek C, Schandelmeier P, Tscherne H. Distal femoral fractures. Unfallchirurg. 1996; 90:2. [PubMed]
5. Albert MJ.SupracondylarFractures of the Femur. J Am AcadOrthop Surg.1997 May;5(3):163-171. [PubMed]
6. Ruedi T, Murphy WM (2000) AO Principles of Fracture Management. Vol. 1. Thieme: Stuttgart-New York. [PubMed]
7. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 1979 Jan-Feb;(138):77-83.
8. Smith WR, Ziran BH, Anglen JO, Stahel PF.Lockingplates: tips and tricks.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2007 Oct;89(10):2298-307. [PubMed]
9. Zlowodzki M, Williamson S, Cole PA, Zardiackas LD, Kregor PJ.Biomechanicalevaluation of the lessinvasivestabilization system, angledbladeplate, and retrogradeintramedullarynail for the internal fixation of distalfemur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004 Sep;18(8):494-502. [PubMed]
10. Roos EM, Roos HP, Lohmander LS, Ekdahl C, Beynnon BD. Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) and HSS—development of a self-administered outcome measure Orthop Sports Phys Ther 1998;2888-96.
11. Zlowodzki M, Bhandari M, Marek DJ, Cole PA, Kregor PJ. Operativetreatment of acutedistalfemur fractures: systematic review of 2 comparative studies and 45 case series (1989 to 2005). J Orthop Trauma. 2006 May;20 (5):366-71. [PubMed]
12. Carmack DB, Berton RM, Kingston C, Zmurko M, Watson JT, Richardson M. Identification of the optimal intercondylar starting point for retrograde femoral nailing: an anatomic study. J Trauma. 2003 Oct;55(4):692-5.
13. Gellman RE, Paiement GD, Green HD, Coughlin RR. Treatment of supracondylar femoral fractures with a retrograde intramedullary nail. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 1996 Nov;(332):90-7. [PubMed]
14. Watanabe Y, Takai S, Yamashita F, Kusakabe T, Kim W, Hirasawa Y. Second-generation intramedullary supracondylar nail for distal femoral fractures. IntOrthop. 2002;26(2):85-8.
15. Lucas. Quoted by Rockwood CA, Green DP. Fractures in adult,45h ed,Vol.II, pg.1972-93,1996.
16. Schatzker J, Horne G, Waddell J.TheTorontoexperiencewithsupracondylarfracturesoffemur.Injury 6,pg.113-28,1975. [PubMed]
17. Markmiller M, Konrad G, Südkamp N. Femur-LISS and distal femoral nail for fixation of distal femoral fractures: are there differences in outcome and complications? ClinOrthopRelat Res. 2004 Sep;(426):252-7. [PubMed]
18. Henderson CE, Lujan TJ, Kuhl LL, Bottlang M, Fitzpatrick DC, Marsh JL. 2010 mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: healing complications
are common after lockedplating for distal femur fractures. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 2011 Jun;469(6):1757-65. doi: 10.1007/s11999-011-1870-6. Epub 2011 Mar 22. [PubMed]
19. Weight M, Collinge C. Early results of the less invasive stabilization system for mechanically unstable fractures of the distalfemur (AO/OTA types A2, A3, C2, and C3). JOrthop Trauma. 2004 Sep;18(8):503-8. [PubMed]
20. Kregor PJ, Stannard JA, Zlowodzki M, Cole PA. Treatment of distal femur fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 103 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004 Sep;18(8):509-20. [PubMed]
21. Schandelmaier P, Partenheimer A, Koenemann B, Grün OA, Krettek C. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury. 2001 Dec;32 Suppl 3:SC55-63. [PubMed]
22. Schütz M, Müller M, Krettek C, Höntzsch D, Regazzoni P, Ganz R, Haas N. Minimally invasive fracture stabilization of distalfemoral fractures with the LISS: a prospective multicenter study. Results of a clinical study with special emphasis on difficult cases. Injury. 2001 Dec;32 Suppl 3:SC48-54. [PubMed]
CITATION
DOI: 10.17511/ijoso.2017.i04.05
Published: 2017-12-31
How to Cite
Sudhir Shroff, A., Sahebrao Bhamare, D., Herode, P., Hansraj Sadaria, M., & Mohan Patel, J. (2017). Comparison of outcomes of supracondylar femur fractures treated with locking compression plate vs supracondylar nail. Surgical Review: International Journal of Surgery, Trauma and Orthopedics, 3(4), 120- 126. https://doi.org/10.17511/ijoso.2017.i04.05
Section
Original Article


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

