Study of gall s tone composition in North Karnataka
Abstract
Introduction: Gall stone disease is common problem in Indian subcontinent. While majority of gallstone disease are cholesterol in north India (similar to western world) they are predominantly pigment or mixed type in south India. There are recent reports of changing trends in composition of gallstones with a shift towards cholesterol gall stones especially in south Asian countries, and this has been attributed to changes in life style and dietary factors.
Material and Methods: Descriptive analytic study were conducted on39 gallstones from KIMS, HUBLI hospital were analysed by semiquantitative titrimetric and colourimetric methods over a period of 18 months from dec 2014 to 2016.The proportion of different types of gallstones was described using 95% confidence interval based on exact method.
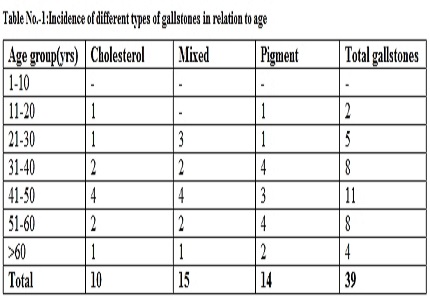
Results: The biliary calculi collected from 39 gallstone patients were divided into 3 groups based on their colour: cholesterol calculi, mixed calculi and pigment calculi. Out of the 39 stones collected , 15 were mixed calculi, 14 were pigment calculi and 10 were cholesterol calculi indicating the incidence of gallstones in the studied population from KIMS, Hubli as follows : Mixed calculi (38%) > pigment calculi ( 36%)> cholesterol calculi (26%). The incidence of gallstone was higher in age group 41-50 yrs followed by 51- 60 yrs and 31-40 yrs in which females were higher than males.
Conclusion: A quantitative chemical analysis of total cholesterol, total bilirubin, fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, bile acids, soluble proteins, sodium potassium, magnesium, copper, oxalate and chlorides of biliary calculi (10 cholesterol, 15 mixed and 14 pigment) retrieved from surgical operation of 39 patients from KIMS, Hubli hospital was carried out. Although total cholesterol was a major component of cholesterol, mixed and pigment gall stone in KIMS, Hubli, the content of most of the other lipids, cations and anions was different in different gall stones indicating their different mechanism of formation.
Downloads
References
2. Bartoli E, Capron JP. Epidemiology and natural history of cholelithiasis.Rev Prat. 2000 Dec 1;50(19):2112-6. [PubMed]
3. Kalloo AN, Kantsevoy SV. Gallstones and biliary disease.Prim Care. 2001 Sep;28(3):591-606, vii. [PubMed]
4. Kratzer W, Mason RA, Kächele V. Prevalence of gallstones in sonographic surveys worldwide.J Clin Ultrasound. 1999 Jan;27(1):1-7. [PubMed]
5. Walker TM, Hambleton IR, Serjeant GR. Gallstones in sickle cell disease: observations from The Jamaican Cohort study.J Pediatr. 2000 Jan;136(1):80-5.
6. Akute OO, Marinho AO, Kalejaiye AO, Sogo K. Prevalence of gall stones in a group of antenatal women in Ibadan, Nigeria. Afr J Med Med Sci. 1999;28(3-4):159–161. [PubMed]
7. Kalloo AN, Kantsevoy SV. Gallstones and biliary disease.Prim Care. 2001 Sep;28(3):591-606, vii. [PubMed]
8. Stringer MD, Taylor DR, Soloway RD. Gallstone composition: are children different?J Pediatr. 2003 Apr;142(4):435-40. [PubMed]
9. Kim MH, Lim BC, Myung SJ, Lee SK, Ohrr HC, Kim YT, Roe IH, Kim JH, Chung JB, Kim CD, Shim CS, Yun YB, Min YI, Yang US, Kang JK. Epidemiological study on Korean gallstone disease: a nationwide cooperative study.Dig Dis Sci. 1999 Aug;44(8):1674-83. [PubMed]
10. Allain CC, Poon LS, Chan CS, Richmond W, Fu PC. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol.Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470-5. [PubMed]
11. Bucolo G, David H. Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes.Clin Chem. 1973 May;19(5):476-82.
12. Lowry OH, Rosebrough NI, Farr Al, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265-75. [PubMed]
13. Chandran P, Kuchhal NK, Garg P, Pundir CS. An extended chemical analysis of gallstone.Indian J ClinBiochem.2007Sep;22(2):145-50. doi: 10.1007/BF02913334. [PubMed]
14. Jaraari AM, Jagannadharao P, Patil TN Quantitative analysis of gallstones in Libyan patients. Libyan J Med. 2010 Jan 7;5. doi: 10.4176/091020. [PubMed]
15. Hussain SM, Al-Jashamy KA. Determination of chemical composition of gallbladder stones and their association with induction of cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(11):6257-60.
16. Atamanalp SS, Keles MS The effects of serum cholesterol, LDL, and HDL levels on gallstone cholesterol concentration. Pak J Med Sci. 2013 Jan;29(1):187-90.
17. Smith JL, Nathanson LK, Riottot M. Effect of statins on biliary lipids and cholesterol gallstones. J FürKardiologie. 2002;9:295–8.
18. Portincasa P, Di Ciaula A, Vendemiale G, Palmieri V, Moschetta A, Vanberge-Henegouwen GP, Palasciano G. Gallbladder motility and cholesterol crystallization in bile from patients with pigment and cholesterol gallstones. Eur J Clin Invest. 2000 Apr; 30(4):317-24.
19. AulakhR, Mohan H, Attri AK, Kaur J, Punia RP. A comparative study of serum lipid profile and gallstone disease.Indian JPatholMicrobiol.2007Apr;50(2):308-12. [PubMed]
20. Hassler KR, Jones MW. Gallbladder, Cholecystectomy, Laparoscopic.StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2017-.2017 Oct 16.
21. Ramana Ramya J1, Thanigai Arul K Chemical and structural analysis of gallstones from the Indian subcontinent. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017 Sep 1;78:878-885. [PubMed]
22. Jayanthi V, Sarika S, Varghese J, Vaithiswaran V, Sharma M, Reddy MS, Srinivasan V, Reddy GM, Rela M, Kalkura S. Composition of gallbladder bile in healthy individuals and patients with gallstone disease from north and South India.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep;35(5):347-353. Epub 2016 Sep 16. [PubMed]


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

