A Retrospective Comparative Analytical Study Between Open And Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Abstract
Aim and Background: Gall stone disease is prevalent in Indian scenario, and with introduction ofLaparoscopic Surgery in surgical domain, there is a change in preference of patients for LaparoscopicCholecystectomy. This study aimed to analyze conventional cholecystectomy and laparoscopiccholecystectomy concerning selection of patients, operative difficulties, duration of surgery,operative complications, postoperative analgesia, postoperative hospital stay, morbidity andmortality, and lastly, patients feedback after surgery.
Methodology: Patients were admitted throughSOPD, thoroughly assessed by necessary investigations and PAC fitness, valid informed consent forparticular procedure was obtained after pros and cons of said procedure were explained in details topatients and their party
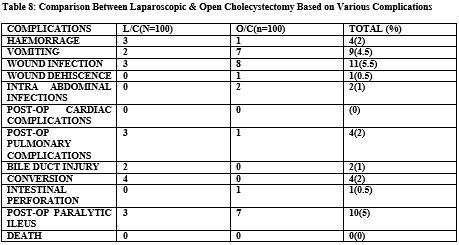
Results: We found more female patients. It is also observed that inoperation time for Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy was significantly less than Open cholecystectomyprocedure. Most important observation of this study is that duration of postoperative pain andanalgesia required was considerably less in Laparoscopic cholecystectomy group than opencholecystectomy. Duration of hospital stay of patients who underwent Laparoscopic surgery had ahospital stay of fewer than four days, while those who underwent open surgery had more thanseven days of holiday. Also found that 1% of patients who underwent open cholecystectomy hadbleeding and 8 % with wound infection. Whereas in Laparoscopic surgery, complication rate wasfound to be 3 % for bleeding, which was minimal and 3 % for wound infection. Conversion rate inLiterature in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy ranges from 3% to 15% in well-trained hands.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy were reduced postoperative pain and less analgesicintake, reduced hospital stay, fewer wound complications, rapid recovery, and early return to normalwork. Open Cholecystectomy is preferred method in case of difficult cholecystectomy.
Downloads
References
2. Khuroo MS, Mahajan R, Zargar SA, Javid G, Sapru S (1989). Prevalence of biliary tract disease in India; a sonogrphic study in adult population in Kashmir. GUT30 : 201-205
3. 3Llis H (2009) John stoughBobbs: Father of Gall Bladder Surgery . Br J Hosp Med ( Lond) 70 : 650
4. Traverso LW (1976) Carl Langenbuch and the first cholecystectomy . [Internet ] Americaan Journal of Surgery p – 81-82
5. JiW ,LiLt , LiJs, Role of subtotal Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the treatment of complicated cholecystitis. Hepatopancreatic Dis Int 2006;5(4):584-9
6. Cuschieri A, Laparoscopic cholecystectomy JR all SurgEdinb 1999; 44: 187-92
7. Lan Cm, Muny FE, Cuschieri A. Increased cholecystectomy rate after the introduction of Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in Scotland. Gut 1996; 38: 282-4
8. Wayland WU, Gatter T. Lap chole; The Austrian Experience . JR coll, Surg Edinb1993;38(3);152
9. 9 Mc Sherry CK, open cholecystectomy, Am J Surg 1993; 165:435 – 39
10. Paulino-Netto A ( 1993) A review of 391 selected open cholecystectomies for comparision with Laparoscopic cholecystectomy . Am J Surg 166; 71-73
11. Cheslyn –Curtis ,Russel RC 91991) New trends in Gall stone management . Br J Surg 78: 143-149
12. Neugebauer E, TroidH, Spangenberger W, Dietrich A, Lefring R and the cholecystectomy study group. Conventional verses Laparoscopic cholecystectomy at the randomized trial. Br J Surg 1991; 78: 150-4
13. Nathganson LK, Shims S, Cuschieri A, Laparoscopic cholecystectomy; the Dundee experience br J Surg 1919; 78: 155-9
14. Oslen DO Mini versus Laparoscopic cholecystectomyAm J Surg 1993; 165: 440 - 43
15. Dirksen CD, Scmiz RF , Hans KM, Nierman FH, Hooquenboong LJ, GoPM Ambulatory Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy is as effective as hospitalisation from a social perspective and less expensive . Ned JijdschrGeneesh 2001; 15: 2434 -39
16. Muhe E (1992) Long – term follow up after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy . Endoscopy 24: 754-758
17. Janik ,Rajan PS, Sendhilkumar K, Palinivelu C (2006) Twenty years after Enrich Muhe : Persisting controversies with the gold standard of Laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Journal of Minimal Access Surgery 2 : 49-58
18. Neugebauer E, Troid IH, Spangenbeuger W, Dietrich A, Lefring R and the cholecystectomy study group . Conventional versus Laparoscopic cholecystectomy and the randomized trial. Br J Surg 1991; 78: 150-4
19. Lan CH, Murray FE ,Cuscheiri A . Increased Cholecystectomy rate aftr the introduction of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy in Scotland . Gut 1996; 38: 282-4
22. WaldnerH ;Laproscopic versus open cholecystectomy in acute cholecystitis. Langen Becker Arch, ChirsupplKongressbd 1997; 44: 1177-9
23. Prospective comparison of Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a community Hospital: Foster , DSWV Med J , 1995; 91(6) 270-272
24 Phillips E . Carroll B ; Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy in Acute cholecystitis. Am Surg . 1992, 58; 273-276
25(26) Carbajo CM, Martin DOJ, Blanco AJ, Cuesta DLLC, Atienza SR, Inglada GL, Vaquero PC, Surgical treatment of Acute cholecystitis in the Laparoscopic age. A comparitivestudy : Laparoscopic against Laparotomy : Rev. Esp. Enfeen. Dig 1998:90(11)788-93
26 VermaGR . Laparoscopic versus open cholecystectomy . Indian J gastroenterology , 1997
27. Stevens HP ,Vande Berg M ; Rusler CH, Wereldsura JC; Clinical and financial aspcts of cholecystectomy . Laparoscopic verses open technique. World J Surg 1997; 21(1): 91-6 Discussion 96-7.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

