Corrective Osteotomy in cubitus varus deformity in children: A prospective study
Abstract
Background and Aim: Cubitus varus deformity is the most common late complication after supracondylar fracture of the distal humerus in children, incidence varying from 4% to 58%. The present study was done to evaluate the results of dome osteotomy.
Material and Methods: This prospective study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital over 16 months. In all patients humerus-elbow wrist angle was measured on both sides and the correction needed was calculated. The lateral condyle prominence index (LCPI) was calculated by anteroposterior view radiographs of the deformed and the normal elbow in full extension by (AB-BC)/AC. Dome osteotomy with para triceps approach was used. Pre and post-operative carrying angle of elbow, range of motion and lateral prominence indices were compared.
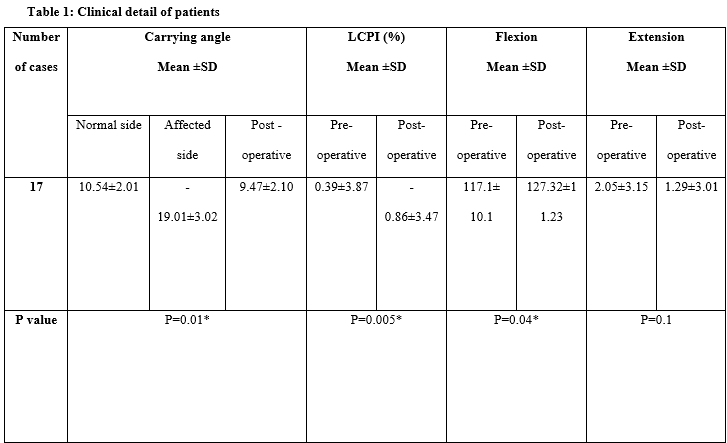
Results: The age of patients ranged from 3 to 15 years with a mean age of 8.47±3.14 years. Preoperative carrying angle of normal side ranged from 80 to 140 and that of effected side ranged from -23 to -13 and the difference was statistically significant (p<0.05). LCPI ranged from -8.4 to 5.9%. The majority of cases had LCPI >2.7%. As compared to, an improvement in carrying angle at defect side was observed to be 28.41±2.15 which was significant (p<0.05). At baseline mean LCPI was 0.39±3.87% which changed to -0.86±3.47%, the mean change of this was significant (p=0.01). baseline
Conclusion: Dome osteotomy is a relatively technically demanding technique for correction of cubitus varus deformity but with a better functional outcome without being associated with lateral condyle prominence.
Downloads
References
2. McBride DJ, Ramamurthy C, Laing P. The hind foot: calcanealand talar fractures and dislocation – Part 1: Fractures of thecalcaneum. CurrOrthop 2005;19:94–100.
3. Thordarson DB, Krieger LE. Operative vs. nonoperative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus: a prospective randomized trial. Foot Ankle Int. 1996 Jan;17(1):2-9. doi: 10.1177/107110079601700102.
4. Järvholm U, Körner L, Thorén O, Wiklund LM. Fractures of the calcaneus. A comparison of open and closed treatment. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984 Dec;55(6):652-6. doi: 10.3109/17453678408992416.
5. Thornes BS, Collins AL, Timlin M, Corrigan J. Outcome of calcaneal fractures treated operatively and non-operatively. the effect of litigation on outcomes. Ir J Med Sci. 2002 Jul-Sep;171(3):155-7. doi: 10.1007/BF03170505.
6. Mcbride, Donald J., C. Ramamurthy, and Patrick Laing. "(ii) The hindfoot: Calcaneal and talar fractures and dislocations—Part I: Fractures of the calcaneum." Current Orthopaedics 19.2 (2005): 94-100.
7. Essex-Lopresti P. The mechanism, reduction technique, and results in fractures of the os calcis. Br J Surg. 1952 Mar;39(157):395-419. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18003915704.
8. Cave EF. Fracture of the os calcis--the problem in general. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1963;30:64-6.
9. Rockwood, Green’s. Fractures in Adults, 8th edition.
10. Mostafa MF, El-Adl G, Hassanin EY, Abdellatif MS. Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2010 Aug;5(2):87-95. doi: 10.1007/s11751-010-0082-z.
11. Tornetta P 3rd. The Essex-Lopresti reduction for calcaneal fractures revisited. J Orthop Trauma. 1998 Sep-Oct;12(7):469-73. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199809000-00007.
12. Tornetta P 3rd. Percutaneous treatment of calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000 Jun;(375):91-6. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200006000-00011.
13. Szabo, Robert M., and Richard A. Marder. Chapman's orthopaedic surgery. Ed. Michael W. Chapman. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001.
14. Wilson, James Noel, ed. Watson-Jones fractures and joint injuries. Elsevier India, 2009.
15. Buckley R, Tough S, McCormack R, Pate G, Leighton R, Petrie D, Galpin R. Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002 Oct;84(10):1733-44. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200210000-00001.
16. Buckley RE, Meek RN. Comparison of open versus closed reduction of intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a matched cohort in workmen. J Orthop Trauma. 1992;6(2):216-22. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199206000-00014.
17. Besse, J. L., Avaro, J. P., Chotel, F., Lerat, J. L., & Moyen, B. Calcaneal intra-articular fracture osteosynthesis: Clinical and radiological prospective study of 31 cases. Foot and ankle surgery, 12.1 (2006): 19-27.
18. Song KS, Kang CH, Min BW, Sohn GJ. Preoperative and postoperative evaluation of intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus based on computed tomography scanning. J Orthop Trauma. 1997 Aug;11(6):435-40. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199708000-00013.
19. Zwipp H, Tscherne H, Thermann H, Weber T. Osteosynthesis of displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. Results in 123 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993 May;(290):76-86.
20. Paley D, Hall H. Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A critical analysis of results and prognostic factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993 Mar;75(3):342-54. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199303000-00005.
21. Herscovici D Jr, Widmaier J, Scaduto JM, Sanders RW, Walling A. Operative treatment of calcaneal fractures in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005 Jun;87(6):1260-4. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.D.01765.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

