Laparoscopic Anterior 180° Partial Fundoplication - Indian Perspective
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate Laparoscopic anterior 180° partial fundoplication for its good long-term relief for symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease and association with adverse effects.
Methods:
Study design: Prospectively evaluated case series.
Settings: Tertiary care centers
Patients: The clinical outcomes were determined for all patients who had undergone a laparoscopic anterior partial fundoplication by us between January 1, 2013 to March 31, 2021.
Interventions: Clinical outcome, complications, and follow-up after laparoscopic anterior 180° partial fundoplication was obtained using a structured questionnaire.
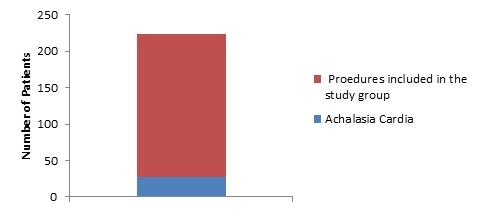
Results and Discussion: 228 procedures were performed. The outcome at 0 to 8 years (mean, 4 years) follow-up was determined for 195 patients. 1 death was linked to the laparoscopic procedure and 2 patients died during follow-up due to unrelated causes. For 186 patients (95%) with clinical outcome data at late follow-up, gastroesophageal reflux symptoms were significantly improved following surgery and were well controlled in 9 patients (4.5%). In a subset of 85 patients with more than 5 years of follow-up, relief of heartburn was found in 59 patients (69%). Incidence and severity of heartburn were reduced after surgery in 22 patients (26%), decreased dyspepsia in 80 patients (94%). Normal belching was preserved in 84 patients (99%) and almost all patients were able to eat normally.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic anterior 180° partial fundoplication is an effective procedure for the surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux and is associated with a high rate of patient satisfaction at late follow-up. Compared to Nissen's fundoplication it is as good as control of recurrent reflux as well as reduced adverse effects. The patient goes home in 3-4 days. Hence we recommend it as the procedure of choice for reflux symptoms.
Downloads
References
DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Albertucci M. Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):9-20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00002.
Crookes, P. F., & DeMeester, T. R. (1994). Does Toupet fundoplication out-perform the Nissen procedure as the operation of choice for gastro-esophageal reflux disease?. Diseases of the Esophagus, 7(4), 265-267.
Lafullarde T, Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Myers JC, Game PA, Devitt PG. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: five-year results and beyond. Arch Surg. 2001 Feb;136(2):180-4. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.136.2.180.
Bammer T, Hinder RA, Klaus A, Klingler PJ. Five- to eight-year outcome of the first laparoscopic Nissen fundoplications. J Gastrointest Surg. 2001 Jan-Feb;5(1):42-8. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(01)80012-3.
Gotley DC, Smithers BM, Rhodes M, Menzies B, Branicki FJ, Nathanson L. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication--200 consecutive cases. Gut. 1996 Apr;38(4):487-91. doi: 10.1136/gut.38.4.487.
Watson DI, Liu JF, Devitt PG, Game PA, Jamieson GG. Outcome of laparoscopic anterior 180-degree partial fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000 Sep-Oct;4(5):486-92. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(00)80091-8.
Watson A, Jenkinson LR, Ball CS, Barlow AP, Norris TL. A more physiological alternative to total fundoplication for the surgical correction of resistant gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg. 1991 Sep;78(9):1088-94. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780918.
Hagedorn C, Lönroth H, Rydberg L, Ruth M, Lundell L. Long-term efficacy of total (Nissen-Rossetti) and posterior partial (Toupet) fundoplication: results of a randomized clinical trial. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002 Jul-Aug;6(4):540-5. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(02)00037-9.
Ludemann R, Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Game PA, Devitt PG. Five-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic total versus anterior 180 degrees fundoplication. Br J Surg. 2005 Feb;92(2):240-3. doi: 10.1002/bjs.4762.
Zornig C, Strate U, Fibbe C, Emmermann A, Layer P. Nissen vs Toupet laparoscopic fundoplication. Surg Endosc. 2002 May;16(5):758-66. doi: 10.1007/s00464-001-9092-8.
Walker SJ, Holt S, Sanderson CJ, Stoddard CJ. Comparison of Nissen total and Lind partial transabdominal fundoplication in the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg. 1992 May;79(5):410-4. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800790512.
Catarci M, Gentileschi P, Papi C, Carrara A, Marrese R, Gaspari AL, Grassi GB. Evidence-based appraisal of antireflux fundoplication. Ann Surg. 2004 Mar;239(3):325-37. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000114225.46280.fe.
Luostarinen M. Nissen fundoplication for reflux esophagitis. Long-term clinical and endoscopic results in 109 of 127 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1993 Apr;217(4):329-37. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199304000-00004.
O'Boyle CJ, Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Myers JC, Game PA, Devitt PG. Division of short gastric vessels at laparoscopic nissen fundoplication: a prospective double-blind randomized trial with 5-year follow-up. Ann Surg. 2002 Feb;235(2):165-70. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200202000-00001.
Broeders JA, Broeders EA, Watson DI, Devitt PG, Holloway RH, Jamieson GG. Objective outcomes 14 years after laparoscopic anterior 180-degree partial versus nissen fundoplication: results from a randomized trial. Ann Surg. 2013 Aug;258(2):233-9. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318278960e.
Du X, Wu JM, Hu ZW, Wang F, Wang ZG, Zhang C, Yan C, Chen MP. Laparoscopic Nissen (total) versus anterior 180° fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Sep;96(37):e8085. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008085.
Broeders JA, Roks DJ, Ahmed Ali U, Watson DI, Baigrie RJ, Cao Z, Hartmann J, Maddern GJ. Laparoscopic anterior 180-degree versus nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Ann Surg. 2013 May;257(5):850-9. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828604dd.
NISSEN R. Eine einfache Operation zur Beeinflussung der Refluxoesophagitis [A simple operation for control of reflux esophagitis]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1956 May 18;86(Suppl 20):590-2. German.
Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Schweiger UM, Pasiut M, Haas CF, Wykypiel H, Pointner R. Long-term results of laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Surg Endosc. 2002 May;16(5):753-7. doi: 10.1007/s00464-001-9103-9.
Booth MI, Jones L, Stratford J, Dehn TC. Results of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication at 2-8 years after surgery. Br J Surg. 2002 Apr;89(4):476-81. doi: 10.1046/j.0007-1323.2002.02074.x.
Watson DI, Jamieson GG. Antireflux surgery in the laparoscopic era. Br J Surg. 1998 Sep;85(9):1173-84. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.1998.00829.x.
Lord RV, Kaminski A, Oberg S, Bowrey DJ, Hagen JA, DeMeester SR, Sillin LF, Peters JH, Crookes PF, DeMeester TR. Absence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in a majority of patients taking acid suppression medications after Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002 Jan-Feb;6(1):3-9; discussion 10. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(01)00031-2.
Wijnhoven BP, Lally CJ, Kelly JJ, Myers JC, Watson DI. Use of antireflux medication after antireflux surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008 Mar;12(3):510-7. doi: 10.1007/s11605-007-0443-1.
Rossetti M, Hell K. Fundoplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in hiatal hernia. World J Surg. 1977 Jul;1(4):439-43. doi: 10.1007/BF01565907.
Ludemann R, Watson DI, Jamieson GG. Influence of follow-up methodology and completeness on apparent clinical outcome of fundoplication. Am J Surg. 2003 Aug;186(2):143-7. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(03)00175-2.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

