Management of Subtrochanteric Femur Fracture Using Proximal Femoral Nail
Abstract
Introduction: Injuries to the femur, the longest bone in the body presents a challenging situation to the orthopedic surgeon. The proximal femoral intramedullary devices are useful for the treatment of isolated pathological lesions in the subtrochanteric region. Biomechanically, the nail can withstand between 3to 5 times body weight. Hence the present study was planned to study the management of these fractures with the proximal femoral nail.
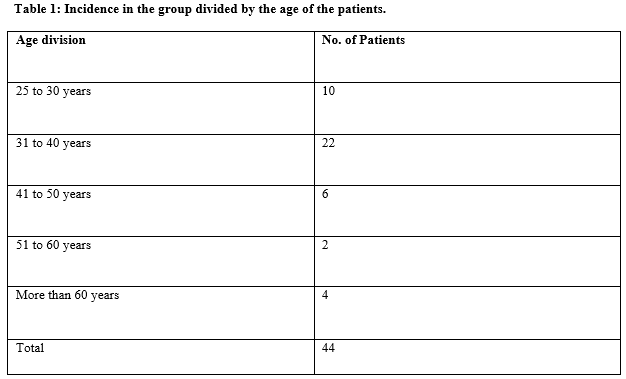
Materials and Methods: A total of 44 patients with proximal femoral fractures of the subtrochanteric region admitted in the department were included in the study. Patients age more than 25 years and diagnosed with subtrochanteric femur fracture were included in the study.
Results: The age of the patients was more than 25 years. There were 34 males and 10 females included in the study. In the clinical evaluation as per the functional Grading of the patient as per Kyle’s Criteria excellent and good results were considered satisfactory, whereas fair and poor results were considered unsatisfactory. In this series 92%, satisfactory results were obtained.
Conclusion: Proximal femur nail (PFN) is an effective device in the management of complex femoral fractures. The use of PFN in such fractures provides various advantages: Closed procedure, Minimal soft tissue damage. It offers superior stabilization than other currently used methods of internal fixation. The use of PFN is technically demanding and needs expertise. Complications can be avoided by proper operative techniques. Early postoperative mobilization and physiotherapy improve the results of PFN.
Downloads
References
Civil I, Morton J, De Angelis C, Drazen J, Frizelle F, Haug C, et al. This Issue of the Journal. NZMA 2004, 117:1.
Salminen S. Femoral shaft fractures in adults: epidemiology, fracture patterns, nonunions, and fatigue fractures. 2005.
Huiskes R, Res COR. The various stress patterns of press-fit, ingrown, and cemented femoral stems. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(261):27-38.
Winquist R, Hansen S, Clawson D. Closed intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. A report of five. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(4):529-539.
Termanini Z: Dynamic intramedullary compression nailing. Google Patents, 1980.
Hammad A, Abdel-Aal A, Said HG, Bakr H. Total hip arthroplasty following failure of dynamic hip screw fixation of fractures of the proximal femur. Acta Orthopædica Belgica. 2008;74(6):788-792.
Kamalahassan G, Kolla S. Management of Extracapsular Fractures of Hip with Proximal Femoral Nailing. J Dent Med Sci. 2016;15(6):75-78.
Michaëlsson K, Weiderpass E, Farahmand BY, Baron JA, Persson P-G, Ziden L, et al. Differences in risk factor patterns between cervical and trochanteric hip fractures. Osteoporosis Int. 1999;10(6):487-494. doi: 10.1007/s001980050259.
Derrick TR, Edwards WB, Fellin RE, Seay JF. An integrative modeling approach for the efficient estimation of cross sectional tibial stresses during locomotion. J Biomech. 2016;49(3):429-435. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2016.01.003.
Jiang LS, Shen L, Dai LY. Intramedullary fixation of subtrochanteric fractures with long proximal femoral nail or long gamma nail: technical notes and preliminary results. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2007;36(10):821-826.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

