Profile of vitamin-D deficiency patients in a tertiary care centre, Bhopal: causes and its implications in health
Abstract
Introduction: Vitamin D deficiency is widespread in individuals irrespective of their age, gender, race and geography. The aim of this study was to assess the status of Vitamin D deficiency in various age group in the people visiting Chirayu Medical College and Hospital, Bhopal for their routine health check-up.
Material and Methods: This study was done in the department of Orthopaedics and department of Biochemistry, Chirayu Medical College and Hospital Bhopal. The study comprised of the total of 100 subjects. Five millilitre of venous blood was collected from subjects in plain vials (red top tube) and the serum Vitamin D level was assessed by ELFA method using Biomeriuxminividas.
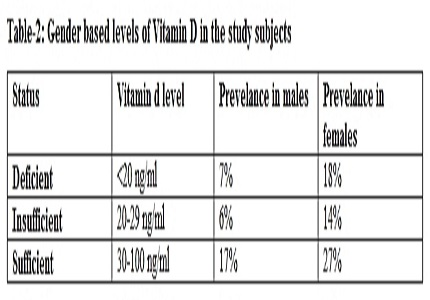
Results: Among the 100 individuals studied in this study there was 66 Females and 34 Males. Among the study group studied it was found that approx. 25% of the total individuals studied are Vitamin D deficient i.e. having serum vitamin D level <20 ng/ml. 20% of the individuals in study group have insufficient vitamin D level i.e. between 20-29 ng/ml. 44% of the total individuals studied have sufficient Vitamin D level (between 30-100 ng/ml) in their sera but in this 44% individuals approx. 11% individuals have their serum vitamin D level in the borderline normal range i.e. between 30-40ng/ml.
Conclusion: As Vitamin D deficiency affects all age groups, therefore, strategies such as increasing awareness among masses about adequate exposure to sunlight, rich dietary sources of vitamin D and fortification of foods with Vitamin D which are consumed by majority of Indian population irrespective of the socio-economic status can be adopted and implemented for prevention and control of Vitamin D deficiency throughout the nation.
Downloads
References
2. G R, Gupta A. Fortification of foods with vitamin D in India. Nutrients. 2014 Sep 12;6(9):3601-23. doi: 10.3390/nu6093601. [PubMed]
3. Khadilkar AV. (2010) Vitamin D deficiency in Indian Adolescents. Indian Paediatr 47:756-757.
4. Ekbote VH, Khadilkar AV, Mughal MZ, Hanumante N, Sanwalka N, Khadilkar VV, Chiplonkar SA, Kant S, Ganacharya R. Sunlight exposure and development of rickets in Indian toddlers. Indian J Pediatr. 2010 Jan;77(1):61-5. doi: 10.1007/s12098-009-0263-2.
5. Agarwal KS, Mughal MZ, Upadhyay P, Berry JL, Mawer EB, Puliyel JM. The impact of atmospheric pollution on vitamin D status of infants and toddlers in Delhi, India. Arch Dis Child. 2002 Aug;87(2):111-3. [PubMed]
6. Hazell TJ, DeGuire JR, Weiler HA. Vitamin D: an overview of its role in skeletal muscle physiology in children and adolescents. Nutr Rev. 2012 Sep;70(9):520-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00510.x. [PubMed]
7. Thacher TD, Clarke BL. Vitamin D insufficiency. Mayo Clin Proc. 2011 Jan;86(1):50-60. doi: 10.4065/mcp.2010.0567. [PubMed]
8. Zittermann A, Schleithoff SS, Tenderich G, Berthold HK, Körfer R, Stehle P. Low vitamin D status: a contributing factor in the pathogenesis of congestive heart failure? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Jan 1;41(1):105-12.
9. Report of Joint FAO/ WHO expert Consultation on vitamin and mineral requirement in human nutrition: bangkok 1998. Second Edition FAO Rome,2004.
10. Londhey V. Vitamin D deficiency: Indian scenario. J Assoc Physicians India. 2011 Nov;59:695-6. [PubMed]
11. Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007 Jul 19;357(3):266-81. [PubMed]
12. Kendrick J, Targher G, Smits G, Chonchol M. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D deficiency is independently associated with cardiovascular disease in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Atherosclerosis. 2009 Jul;205(1):255-60. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.10.033. Epub 2008 Nov 11.
13. Sachan A, Gupta R, Das V, Agarwal A, Awasthi PK, Bhatia V. High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among pregnant women and their newborns in northern India. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005 May;81(5):1060-4. [PubMed]
14. Goswami R, Gupta N, Goswami D, Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Kochupillai N. Prevalence and significance of low 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in healthy subjects in Delhi. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Aug;72(2):472-5. [PubMed]
15. Jones G, Prosser DE, Kaufmann M. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1): its important role in the degradation of vitamin D. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Jul 1;523(1):9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.11.003. Epub 2011 Nov 12. [PubMed]
16. Liao E. FGF23 associated bone diseases. Front Med. 2013 Mar;7(1):65-80. doi: 10.1007/s11684-013-0254-6. Epub 2013 Mar 9. [PubMed]
17. Harinarayan CV, Ramalakshmi T, Venkataprasad U. High prevalence of low dietary calcium and low vitamin D status in healthy south Indians. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2004;13(4):359-64. [PubMed]
18. Tandon N, Marwaha RK, Kalra S, Gupta N, Dudha A, Kochupillai N. Bone mineral parameters in healthy young Indian adults with optimal vitamin D availability. Natl Med J India. 2003 Nov-Dec;16(6):298-302. [PubMed]
19. Khandare AL, Harikumar R, Sivakumar B. Severe bone deformities in young children from vitamin D deficiency and fluorosis in Bihar-India. Calcif Tissue Int. 2005 Jun;76(6):412-8. Epub 2005 May 19. [PubMed]
20. Hossein-nezhad A, Spira A, Holick MF. Influence of vitamin D status and vitamin D3 supplementation on genome wide expression of white blood cells: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058725. Epub 2013 Mar 20. [PubMed]
21. Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007 Jul 19;357(3):266-81. [PubMed]
22. Mithal A, Wahl DA, Bonjour JP, Burckhardt P, Dawson-Hughes B, Eisman JA, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Josse RG, Lips P, Morales-Torres J; IOF Committee of Scientific Advisors (CSA) Nutrition Working Group. Global vitamin D status and determinants of hypovitaminosis D. Osteoporos Int. 2009 Nov;20(11):1807-20. doi: 10.1007/s00198-009-0954-6. Epub 2009 Jun 19. [PubMed]


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

