Comparison of clinical, radiological, and functional outcome of closed fracture of distal third tibia treated with nailing and plate osteosynthesis
Abstract
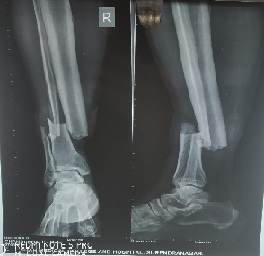
Aim: This is a prospective study of 30 patients with distal tibia fracture (Closed extra-articular distal third tibia fractures - 4 to 11cm from tibial plafond) who underwent surgical fixation were included in this study after excluding compound, pathological and pediatric fractures.
Materials and Methods: 15 underwent closed intramedullary interlocking nail and 15 were treated with plate osteosynthesis (MIPO).
Results: The age distribution ranged from 23 to 68 years with the mean age of 39.4 years. The mode of injury in all patients was due to vehicle accidents. All 30 patients were classified according to AO classification of which 15 belonged to A1, 14 belonged to A2, and 1 belonged to A3. The time of fixation from injury varied from 6 hours to 18 days.
Conclusion: Plate osteosynthesis by minimally invasive technique and Intramedullary interlocking nailing is an equally effective method of stabilization for distal tibia fracture when considering the union rates and final functional outcome. However, malunion, nonunion and secondary procedures were more frequent after intramedullary interlocking nail. In MIPO platting Infection followed by an exposed plate occurs in 2 patients. Randomized prospective evaluation of distal tibia fractures may clarify the efficacy of plate versus nail treatment and optimize patient care.
Downloads
References
Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Campbell’s Opertive Orthopaedics. 9th ed. 2001, Chapter 34, p. 2675‑2678.
Nork SE, Schwartz AK, Agel J, Holt SK, Schrick JL, Winquist RA. Intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1213-1221. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.C.01135.
Guo JJ, Tang N, Yang HL, Tang TS. A prospective, randomised trial comparing closed intramedullary nailing with percutaneous plating in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(7):984-988. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.92B7.22959.
Dogra AS, Ruiz AL, Thompson NS, Nolan PC. Dia-metaphyseal distal tibial fractures—treatment with a shortened intramedullary nail: a review of 15 cases. Injury. 2000;31(10):799-804. doi: 10.1016/s0020-1383(00)00129-7.
Gustilo T, Shaw AD. Knee pain after intramedullary tibial nailing: its incidence, etiology, and outcome. J Orthop Trauma. 1997;11(2):103-105. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199702000-00006.
Mohammed A, Saravanan R, Zammit J, King R. Intramedullary tibial nailing in distal third tibial fractures: distal locking screws and fracture non-union. Int Orthop. 2008;32(4):547-549. doi: 10.1007/s00264-007-0356-3.
Collinge C, Kuper M, Larson K, Protzman R. Minimally invasive plating of high‑energy metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(6):355-361. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3180ca83c7.
Collinge C, Protzman R. Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(1):24-29. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181ac3426.
Megas P, Zouboulis P, Papadopoulos AX, Karageorgos A, Lambiris E. Distal tibial fractures and non-unions treated with shortened intramedullary nail. Int Orthop. 2003;27(6):348-351. doi: 10.1007/s00264-003-0499-9.
Egol KA, Weisz R, Hiebert R, Tejwani NC, Koval KJ, Sanders RW. Does fibular plating improve alignment after intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibia fractures? J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(2):94-103. doi: 10.1097/01.bot.0000199118.61229.70.
Freedman EL, Johnson EE. Radiographic analysis of tibial fracture malalignment following intramedullary nailing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;(315):25-33.
Im GI, Tae SK. Distal metaphyseal fractures of tibia: A prospective randomized trial of closed reduction and intramedullary nail versus open reduction and plate and screws fixation. J Trauma. 2005;59(5):1219-1223; discussion 1223. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000188936.79798.4e.
Iqbal HJ, Pidikiti P. Treatment of distal tibia metaphyseal fractures; plating versus intramedullary nailing: a systematic review of recent evidence. Foot Ankle Surg. 2013;19(3):143-147. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2013.04.007.
Pugh KJ, Wolinsky PR, McAndrew MP, Johnson KD. Tibial pilon fractures: A comparison of treatment methods. J Trauma. 1999;47(5):937-941. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199911000-00022.
McFerran MA, Smith SW, Boulas HJ, Schwartz HS. Complications encountered in the treatment of pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1992;6(2):195-200. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199206000-00011.
Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): Plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(5):307-311. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e31816ed974.
Tyllianakis M, Megas P, Giannikas D, Lambiris E. Interlocking intramedullary nailing in distal tibial fractures. Orthoped. 2000;23(8):805-808.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

