The effect of Platelet-rich plasma on the repair of sports-related muscle, tendon and ligament injuries
Abstract
Introduction: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment is a developing technology that ambitions to recover the procedure of tissue overhaul via the distribution of bioactive representatives, which will deliver chemotactic, proliferative, and anabolic cellular retorts and improve retrieval of tissue purpose.
Materials and methods: Fifty-three recreational athletes were registered in the study. The patients were enrolled from the Emergency ward in the University Hospital at Parma rendering to a pre-defined procedure. Each patient was evaluated by ultrasound imaging to assess the range and mark of muscle harm. Only grade II lesions were preserved with 3 ultrasound-guided vaccinations of autologous platelet-rich plasma every seven days. Platelet distillate was formed as per the standard methods, with a 10% erraticism in platelet count. The platelet gel for medical use was found by addition thrombin to the distillates beneath regular circumstances. Consequences measured were: pain reduction, muscle function retrieval, and reappearance to sports activity, ultrasound-imaging tissue remedial, relapses, local contagions, and any side effect through the action.
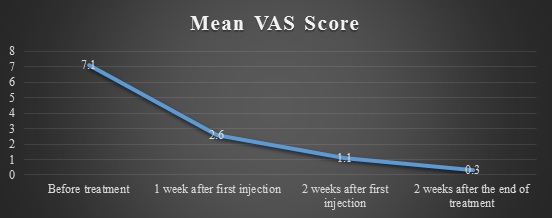
Results: In all cases muscle lesions cured completely on ultrasound-imaging, the sting vanished, and muscle function retrieval was recognized with a reappearance to sports activity. A solo patient had a reversion 1 year after cure.
Conclusion: Platelet-rich plasma vaccinated into the harm site is one of the greatest significant factors interpreting the behavior operative. Rendering to the present consequences, which document complete muscle retrieval and no reversion excluding for one patient, platelet-rich plasma ultrasound-guided vaccination signifies an effective mini-aggressive cure for muscle harm.
Downloads
References
Creaney L, Hamilton B. Growth factor delivery methods in the management of sports injuries: the state of the play. Br J Sports Med. 2008;42(5):314-320.
Kon E, Filardo G, Di Martino A, Marcacci M. PRP to treat sports injuries: evidence to support its use Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(4):516-527.
Engebretsen L, Steffen K, Alsousou J, Anitua E, Bachl N, Devilee R, et al. IOC consensus paper on the use of platelet-rich plasma in sports medicine. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(15):1072-1081.
Borrione P, Di Gianfrancesco A, Pereira MT, Pigozzi F. PRP in muscle healing. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;89(10):854-861.
Kampa RJ, Connell DA. Treatment of tendinopathy: is there a role for autologous whole blood and PRP injection. Int J Clin Pract. 2010;64(13):1813-1823.
Cyriax JH. The pathology and treatment of tennis elbow. J Bone Joint Surg. 1936;18(14):921-940.
Kraushaar BS, Nirschl RP. Tendinosis of the elbow (tennis elbow). Clinical features and findings of histological, immunohistochemical, and electron microscopy studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(2):259-257.
Sharma P, Maffulli N. Tendon injury and tendinopathy: healing and repair. J Bone Joint Surg. 2005;87(1):187-202.
Maffulli N, Longo UG, Denaro V. Novel approaches for the management of tendinopathy. J. Bone Joint Surg. 2010;92(15):2604-2613.
Andia I, Sanchez M, Maffulli N. Tendon healing and PRP therapies. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(10): 1415-1426.
Gaweda K, Tarczynska M, Kryzanowski W. Treatment of Achilles tendinopathy with PRP. Int J Sports Med. 2010;31(8):577-583.
Haake M, König IR, Decker T, Riedel C, Buch M, Müller HH, et al. Extra corporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: A randomized multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84(11):1982-1991.
Bjordal JM, Couppe C, Ljunggren AE. Low level laser therapy for tendinopathy: evidence of a dose response. Phys Ther Rev. 2001;6(2):91-99.
Kon E, Filardo G, Delcogliano M, Russo A, Bondi A, et al. PRP: new clinical application. A pilot study for treatment of jumper’s knee. Injury. 2009;40(6):598–603.
Filardo G, Kon E, Della Villa S, Vincentelli F, Fornasari PM, Marcacci M. Use of PRP for the treatment of refractory jumper’s knee. Int Orthopaed. 2010;34(6):909-915.
Vasseljen O, Jr, Høeg N, Kjeldstad B, Johnsson A, Larsen S. Low level laser versus placebo in the treatment of tennis elbow. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1992;24(1):37-42.
Edwards SG, Calandruccio JH. Autologous blood injections for refractory lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Am. 2003;28(2):272-278.
Landesberg R, Roy M, Glickman RS. Quantification of growth factor levels using a simplified method of platelet-rich plasma gel preparation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(3):297-300.
Mishra A, Pavelko T. Treatment of elbow chronic tendinosis with buffered PRP Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(11):1774-1778.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

