Evaluation of Laboratory risk indicators (LRINEC Sore) for early diagnosis and prognosis in necrotizing fasciitis
Abstract
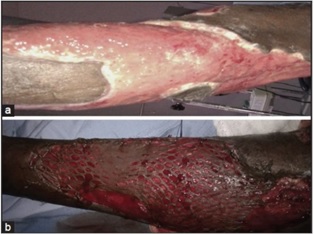
Background: Necrotizing soft tissue infections are rare but potentially fatal involving subcutaneous tissues and fascia. It can progress to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), shock, potential limb loss and death. The present study is an attempt to evaluate the early diagnostic efficacy and prognostic value of laboratory risk indicators (LRINEC scoring system) in necrotizing fasciitis.
Methods: This prospective observational study was conducted onall patients of 18-80year age admitted in the Department of Surgery, PCMS and RC during the study period presenting with any of the clinical features of soft tissue infections.LRINEC SCORE was calculated for each patient using the laboratory values (CRP, WBC, Hb, sodium, creatinine and glucose) that ranged from 0-13Record was made of the final diagnosis and prognosis. Diagnostic and prognostic value of LRINEC score was evaluated using statistical analysis.
Results: The most common site involved was Lower Extremities followed by Upper and Scrotum/Perineum. The study revealed that risk increases with advancing age. The systemic complication was in the intermediate and high-risk case, no one in low-risk case. The conservative treatment was mainly used for the patients with low risk but the surgical intervention was the mainstay of management in the intermediate and high-risk category.
Conclusion: In the present study it can be concluded that LRINEC score, using readily available laboratory data, can serve as a simple and an important tool in predicting the prognosis and risk stratification in cases of necrotizing fasciitis but diagnostic efficacy is not that much reliable.
Downloads
References
Lancerotto L, Tocco I, Salmaso R, Vindigni V, Bassetto F. Necrotizing fasciitis: classification, diagnosis, and management. JTrauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(3):560-566.doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/ta.0b013e318232a6b3
Wong CH, Khin LW, Heng KS, Tan KC, Low CO. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(7):1535-1541.doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000129486.35458.7d.
Majeski J, Majeski E. Necrotizing fasciitis: improved survival with earlyrecognition by tissue biopsy and aggressive surgical treatment. Southampt MedJ 1997;90(11):1065-1068.doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00007611-199711000-00001.
El-Menyar A, Asim M, Mudali I N.,Mekkodathil A, Latifi R, Al-Thani H. The laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing fasciitis (LRINEC) scoring: the diagnostic and potential prognostic role. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2017;25(1):28.doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-017-0359-z.
Avalahalli MG, Muniraja PK, Khalid MS, Kaverappa K, Devaraj L, Rao A. Comparative study of LRINEC score: procalcitonin and LRINEC score: C-Reactive Protein in predicting duration of hospital stay and severity in necrotizing fascitis. J Evolution Med Dent Sci. 2016;5(51):3348-3351.doi:https://doi.org/10.14260/jemds/2016/754.
Kumar N, Garg R, Soni RK, Namdeo R. Correlation of the laboratory risk indicators for necrotizing fasciitis (LRINEC) score with the clinical features and surgical management of necrotizing soft tissue infections. Int Surg J. 2018;5(10):3394-3398.doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20184096.
Soitkar A, Akhtar M, Choudhari A, Deshmukh S. Necrotizing fasciitis: diagnostic and prognostic value of laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing fasciitis score. Int Surg J. 2019;6(5):1750-1755.doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20191901.
Al-Hindawi A, McGhee J, Lockey J, Vizcaychipi M. Validation of the laboratory risk indicator for necrotising fasciitis scoring system (LRINEC) in a Northern European population. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2017;70(1):141-143.doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2016.05.014.
Liao CI, Lee YK, Su YC, Chuang CH, Wong CH. Validation of the laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing fasciitis (LRINEC) score for early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Tzu Chi Med J. 2012;24(2):73-76.doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcmj.2012.02.009.
Neeki MM, Dong F, Au C, Toy J, Khoshab N, Lee C, et al. Evaluating the Laboratory Risk Indicator to Differentiate Cellulitis from Necrotizing Fasciitis in the Emergency Department. West J Emerg Med. 2017;18 (4):684-689.doi:https://dx.doi.org/10.5811%2Fwestjem.2017.3.33607.
Chan T, Yaghoubian A, Rosing D, Kaji A, de Virgilio C. Low sensitivity of physical examination findings in necrotizing soft tissue infection is improved with laboratory values: a prospective study. Am JSurg. 2008;196(6):926-930. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.07.025.
Su YC, Chen HW, Hong YC, Chen CT, Hsiao CT, Chen IC. Laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing fasciitis score and the outcomes. ANZ JSurg. 2008;78(11):968-972. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-2197.2008.04713.x.
Goh T, Goh LG, Ang CH, Wong CH. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br J Surg. 2014;101(1):e119-e125. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.9371.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

