Management of distal femur fractures with locking compression plate
Abstract
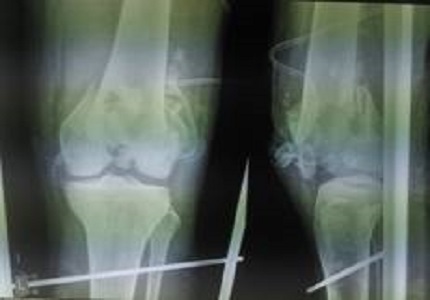
Background: Distal femur fractures are often caused by high energy trauma mainly sustained in road traffic accidents. Open injuries with considerable comminution of condyles and metaphysis are frequently seen. The present study is undertaken to assess outcome of 20 patients of distal femur fractures treated with locking compression plate.
Methods: 20 cases of distal femur fractures in adults treated by locking compression plate were studied. Of the 20 ‘lower end of Femur’ fractures, 4 were Mullers type A3; 2 were Mullers type B1; 6 were Mullers type C1; 4 were Mullers type C2 and remaining 4 were Mullers type C3. All fractures were closed. Maximum age was 68 years and minimum age was 26 years. 16 were male and 4 were female. Results assessed by time for union, range of motion of knee, shortning, varus/valgus deformity and complications.fuctional assessment was done by Neers scoring.
Result: Most common type of distal femur fracture was Mullers type C1. Of 20 patients, 17 patients (85%) showed radiological union within 18 weeks. Average flexion in this study was 105 degree with more than 65% patients having knee range of motion more than 110 degree. Average extensor lag in this study was 5.60 degrees. 3 had shortening, 2 patients had shortening of 15 mm and 1 had shortening of 10mm.varus / valgus malalignment of less than 5 degree seen in 5 cases.4 patient developed superficial infection.only one patient went into delayed union. 80 % excellent and good results were obtained by Neers scoring.
Conclusion: Locking compression plate is an optimal tool for supracondylar fractures of femur. It provides rigid fixation in region of femur, where a widening canal, thin cortices and frequently poor bone stock make fixation difficult. Surgical exposure for plate placement requires significantly less periosteal stripping and soft tissue exposure than that of normal plates.
Downloads
References
2. Schandelmaier P, Partenheimer A, Koenemann B, Grün OA, Krettek C. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury. 2001 Dec;32 Suppl 3:SC55-63. [PubMed]
3. Kregor PJ, Stannard J, Zlowodzki M, Cole PA, Alonso J. Distal femoral fracture fixation utilizing the Less Invasive Stabilization System (L.I.S.S.): the technique and early results. Injury. 2001 Dec;32 Suppl 3:SC32-47.
4. Schütz M, Müller M, Regazzoni P, Höntzsch D, Krettek C, Van der Werken C, Haas N. Use of the less invasive stabilization system (LISS) in patients with distal femoral (AO33) fractures: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005 Mar;125(2):102-8. Epub 2005 Feb 2.
5. Kregor PJ, Stannard JA, Zlowodzki M, Cole PA. Treatment of distal femur fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 103 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004 Sep;18(8):509-20.
6. Martinet O, Cordey J, Harder Y, Maier A, Bühler M, Barraud GE. The epidemiology of fractures of the distal femur. Injury. 2000 Sep;31 Suppl 3:C62-3. [PubMed]
7. Muller ME, Nazarlan S, Koch P, Sdiatzker J. The comprehensive classification of fractures of long bones. Berlin, etc : Springer-Verlag, 1990.
8. Weight M, Collinge C. Early results of the less invasive stabilization system for mechanically unstable fractures of the distal femur (AO/OTA types A2, A3, C2, and C3). J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:503-508.
9. Kregor PJ, stannard JA, Zlowodzki M, et al. treatment of Distal Femur Fractures Using the Less Invasive Stabilization System: Surgical Experience and Early Clunical Results in 103 fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2004 sep;18(8):509-20.
10. Yeap, E.J., and Deepak, A.S., Distal Femoral Locking Compression Plate Fixation in Distal Femoral Fractures: Early Results. Malaysian Orthopedic Journal, 2007; 1 (1). Pp.
12-17. ISSN 1985-2533.
11. Vallier HA, Hennessey TA, Sontich JK, Patterson BM. Failure of LCP condylar plate fixation in the distal part of the femur. A report of six cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006 Apr;88(4):846-53.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

