Comparison of n butyl 2 cyanoacrylate and silk sutures for the minor surgical procedure: a clinical study
Abstract
Background and Aim:The purpose of this study is to compare the clinical responses of intraoral mucosal incisions closed with n-butyl-2- cyanoacrylates with incisions closed with silk sutures.
Materials and Methods: In thirty patients requiring minor oral surgical procedures bilateral mucosal incisions were placed. One side was closed with n-butyl cyanoacrylate and other with silk suture. Postoperatively patients were recalled on 1st, 7th, 14th, and 21st day and evaluated for pain, edema, wound dehiscence, and scar. Results were evaluated using the chi-square test.
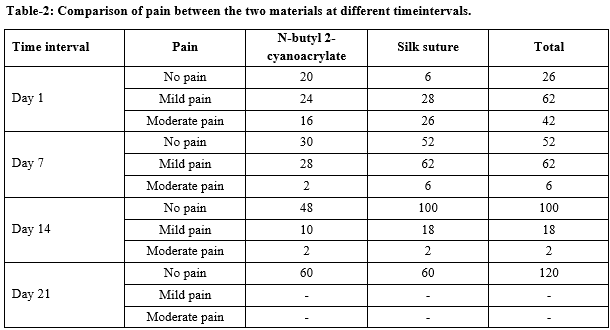
Results: The results showed that there was no statistically significant difference between suture and cyanoacrylate for occurrences of pain, edema, and wound dehiscence, and scar formation. However, the averages time taken for suturing was considerable more than the time taken for cyanoacrylate application.
Conclusion: This study suggests that the efficacy of cyanoacrylate and suture in intraoral wound closure is similar for postoperatively finding like pain, edema, wound dehiscence, and scar formation. However, cyanoacrylate has certain advantages like ease of application, less time consuming, and is well accepted by patients.
Downloads
References
Meakins JL, Masterson BJ, Nichols R. Prevention of postoperative infection. basic surgical operative consideration pp 2005:13-33.
Velvart P, Peters CI, Peters OA. Soft tissue management: suturing and wound closure. Endodontic topics. 2005;11(1):179-195.doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-1546.2005.00165.x.
Ramya H: A clinical comparison of silk sutures and n-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate for closure of mucosal incisions. 2011.
QUAN CJ. Laryngeal Microsurgery-Characterization of Magnesium-Based Microclips for Wound Closure (Doctoral dissertation).
Simon B, Hern H, Marx J: Wound management principles. Marx J, Hockbergr R, Walls R Rosen’s Emergency medicine 8th ed Philadelphia: Saunders. 2014:751-766.
Buckley MJ, Beckman EJ. Adhesive use in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2010;22(1):195-199.doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coms.2009.10.008.
Beldon P: Basic science of wound healing. Surg. 2010;28(9):409-412.doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpsur.2010.05.007.
Nathan HS, Nachlas MM, Solomon RD, Halpern BD, Seligman AM: Nonsuture closure of arterial incisions using a rapidly polymerizing adhesive. Ann Surg. 1960;152(4):648-659.doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-196010000-00009.
Suthar P, Shah S, Waknis P, Limaye G, Saha A, Sathe P. Comparing intra-oral wound healing after alveoloplasty using silk sutures and n-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate. JKorean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;46(1):28-35.doi: https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2020.46.1.28.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

