A study to evaluate the functional outcome of displaced supracondylar humerus fracture in pediatrics treated with closed reduction and k-wire fixation
Abstract
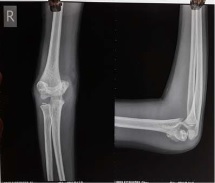
Introduction: Supracondylar fracture of the humerus is the most common elbow injury in children and makes up approximately 60% of all elbow injuries. The purpose of the present study is to evaluate the functional outcome of the displaced supracondylar humerus fracture treated with closed reduction and k-wire fixation by lateral and cross pinning technique.
Material and Method: 50 children with fractures of the supracondylar humerus out of which 30 were boys and 20 were girls taken for prospective study at C.U. Shah Medical College from May 2017 to August 2019 was analyzed clinically and radiologically using Flynn’s criteria. Out of 50 cases 28 patients treated with lateral pinning and 22 patients treated with cross pinning technique based on the surgeon’s preference.
Result: among patients treated with lateral pinning technique 19(68%) had an excellent result, 9(32%) had a good result. Similarly in patients treated with cross pinning technique, 9(41%), 7(32%), 2(9%), 4(18%) had excellent, good, fair, and poor outcomes respectively. 9 patients developed iatrogenic ulnar nerve palsy in cross pinning technique whereas 2 patients developed cubitus varus following cross pinning technique.
Conclusion: Thus it can be concluded that closed reduction and K-wire fixation is an excellent method for the treatment of supracondylar fracture of the humerus with the significant difference in functional outcome between lateral pinning and cross pinning technique. The chances of ulnar nerve palsy increase following cross pinning technique which is not so in the case of lateral pinning. Thus suggesting the use of lateral pinning technique for the treatment of displaced supracondylar fracture of the humerus.
Downloads
References
Herring JA, editor. Fracture about the elbow. In: Tachdjian’s Paediatric Orthopaedics. 3rd ed Vol 3, Philadelphia, W.B. Saunders;2002:2139-2221.
David L. Skaggs and John M. Flynn.Supracondylar fracture of the distal humerus (Chapter 16).In Rockwood and Wilkins Fractures in Children. 8th edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, p 581-628.
Weiland AJ, Meyer S, Tolo VT, Berg HL, Mueller J. Surgical treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Analysis of fifty-two cases followed for five to fifteen years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(5):657-661.
Gartland J. Management of Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Surggynecolobstet 1959;109(2):145-154.
Flynn C. Blind Pinning of Displaced of the Humerus Supracondylar in Children. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1974;56(2):263-272.
Zamzam MM, Bakarman KA, Treatment of displaced supracondylar humeral fractures among children: crossed versus lateral pinning. Injury. 2009;40(6):625-630. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2008.10.029.
Celiker O, Pestilci FI, TuzunerM. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children: analysis of the result in 142 patients. J Orthop Trauma.1990;4(3):265-269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-199004030-00005.
Smith. Deformity following supracondylar fracture humerus. J Bone and Joint Surg. 1960:42A:235.
Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children: treatment by overhead skeletal traction. J PediatrOrthop 1997;17(1):127. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00004694-199701000-00029.
Boyd HB, Attenberg AR. Fracture about elbow in children. Arch Surg. 1944:49:231-234
Sharma A, Walia JSP, Brar BS, Sethi S.Early results of displaced supracondylarfractures of humerus in children treated by closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. Indian JOrthop. 2015;49(5):529-535. https://dx.doi.org/10.4103%2F0019-5413.164039.
Vala GP, Chauhan R, Raiyani DM. AComparative Study of Crossed versus Lateral Pinning in theTreatment of Displaced Extension Type of SupracondylarFractures of the Humerus. GJRA. 2016;5(4): doi: https://www.doi.org/10.36106/gjra.
Naik LG, Sharma GM, Badgire KS. Cross Pinning Versus Lateral Pinning in the Managementof Type III Supracondylar Humerus Fracture in Children. JClin Diagnos Res. 2017;11(8):RC01-RC03. doi: https://doi.org/10.7860/jcdr/2017/28481.10351.
Bharti SR, Magdum AK. A Comparative Study ofCross Pinning Versus Lateral Pinning by Percutaneous K-wire inPaediatric Supracondylar Fractures of Humerus. Int JBiomed Res 2018;9(9):325-329. doi: https://doi.org/10.7439/ijbr.v9i9.4900.
Aronson DD, Prager BI. Supracondylar fractures of humerus inchildren – A Modified technique of closed pinning. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;218:174-184.
Henrikson B. Supracondylar fracture of humerus in children. ActaChirScand. 1956;369:1-72.
Bhuyan BK, Close reduction and percutaneous pinning indisplaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2012;3(2):89-93. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.jcot.2012.09.004.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

