A clinical study to evaluate the outcome of diaphyseal humerus fracture in adult age group treated with anterior biological plating
Abstract
Background: Anterior biological plating is one of the many options to treat diaphyseal humerus fractures in the adult age group. A clinical study was performed to evaluate outcomes over 6 months follow up period in 25 patients.
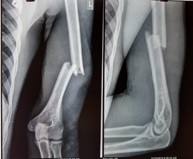
Materials and Methods: The present study included 25 patients of the adult age group having diaphyseal humerus fracture treated with anterior biological plating between February 2018 to June 2019.Pathological, Malunited, and Gustilo Anderson open to grade 3 fractures were excluded from the study. Locking Compression Plating was done in all cases using the MIPO technique after closed indirect reduction. Functional outcome was assessedusing the DASH score at 6 months follow up.
Results: The study consisted of 16 males and 9 females. The mean age was 42.36 years (range: 19-73 years).7 fractures out of 25 were 12A1, 2 were 12A2, 10 were 12A3,2 were 12B1 and 4 were 12B2 based on AO classification. Mean DASH score in the present study was 7.9 with 21 patients achieving excellent DASH Score and 4 patients achieving good DASH score with none of the patients having fair or poor DASH scores.
Conclusion: ABP for mid-shaft humerus fractures is a safe and effective treatment modality yielding high rates of the union, excellent functional recovery, minimal biological disruption, better cosmesis, and superior patient satisfaction.
Downloads
References
Gustilo RB, Anderson JT Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(4):453-458.
Emmett JE, Breck LW: A review and analysis of 11,000 fractures seen in a private practice of orthopaedic surgery, 1937–1956. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958;40-A(5):1169-1175.
Schemitsch EH, Bhandari M, Talbot M: Fractures of the humeral shaft. In Skeletal Trauma: Basic Science, Management and Reconstruction. volume 2. 4th edition. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2008:1593–1594.
Rose SH, Melton LJ 3rd, Morrey BF, Ilstrup DM, Riggs BL: Epidemiologic features of humeral fractures. Clin OrthopRelat Res. 1982,168:24-30.
Brinker MR, O’Connor DP. The incidence of fractures and dislocations referred for orthopaedic services in a capitated population. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(2):290–297.
Ekholm R, Adami J, Tidemark J, Hanson K, Törnkvist H, Ponser S. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus: an epidemiological study of 401 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88-B(11):1469-1473. doi: https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.88b11.17634.
Fracture and Dislocation Classification Compendum. Humerus. JOrthopTrauma. 2018;32(1):S15-16. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000001062.
Hoppenfeld S, deBoer P. Surgical Exposures in Orthopedics. Philadelphia, PA: J.B. Lippincott; 1984.
Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Tscherne H. Distal femoral fractures: Transarticular reconstruction, percutaneous plate osteosynthesis and retrograde nailing [in German].Unfallchirug. 1996; 99:2-1038.
Sarmiento A, Zagorski JB, Zych GA, Latta LL, Capps CA.Functional bracing for the treatment of fractures of the humeral diaphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(4):478-486. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200004000-00003.
Wagner M, Frigg R. AO Manual of fracture management:Internal fixators. Chapters 1.2: Concepts of fracture fixation, 2006.
Baumgaertel F, Buhl M, Rahn BA. Fracture healing in biological plate osteosynthesis Injury. 1998;29(3):C3-C6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-1383(98)95002-1.
Dickson KF, Munz JW. Locked plating: BiomechanicsBiology. Tech Orthop. 2007;22(4):E1-E6.
Wagner M, Frenk A, Frigg R. Locked plating: Biomechanics and biology and locked plating: Clinical indications. Tech Orthop. 2007;22:4.
Apivatthakakul T, Arpornchayanon O, Bavornratanavech S. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture: Is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary report. Injury. 2005;36(4):530-538. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2004.05.036.
Livani B, Belangero W, Andrade K, Zuiani G, Pratali R. Is MIPO in humeral shaft fractures really safe? Postoperative ultrasonographic evaluation. Int Orthop. 2009;33(6):1719-1723. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs00264-008-0616-x.
Zogaib RK,Morgan S,Belangero PS,Fernandes HJA,Belangero WD,Livani B. Minimal invasive osteosynthesis for treatment of diaphyseal transverse humeral shaft fractures. Acta Ortop Bras. 2014;22(2):94-98.doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1413-78522014220200698.
MahajanAS, Kim YG, Kim JH,D’sa P, Lakhani A, Ok HS. Is Anterior Bridge Plating for Midshaft Humeral Fractures a Suitable Option for Patients Predominantly Involved in Overhead Activities? A Functional Outcome Study in Athletes and Manual Laborers. ClinOrthop Surg. 2016;8(4):358-366.doi: https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.358.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

