Comparative evaluation of hydrogel dressing with conventional dressing in diabetic foot ulcers
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetic foot is a common problem in this part of the country. In patients with diabetic foot and pressure ulcers, early intervention with biological therapy will either halt progression or result in rapid healing of these chronic wounds. So here we compare the effectiveness of hydrogel dressing versus conventional dressings in the healing of diabetic foot ulcerations in terms of healing rate, safety, and patient satisfaction.
Material and methods: Prospective case–control study enrolling 40 patients, divided into two groups. Cases (patients treated with hydrogel) and Controls (patients treated with conventional dressings), with an equal number of patients in each group over 12 months period. Diabetic foots were treated until wound closure, either spontaneously, surgically, or until completion of the 8-week period.
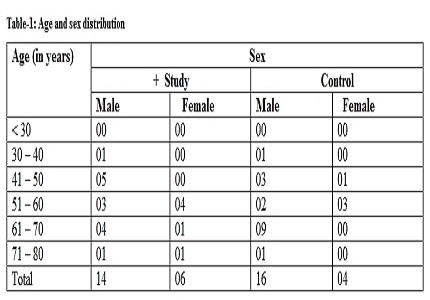
Result: 85% study and 90% control group patients were between the age of 41–70 years. Male to female ratio in study group and control group was 2.33:1 and 4:1 respectively. Duration of stay, amputation rates were statistically significantly reduced as compared to control and after 8 weeks of dressing. In study group complete responders were 80% and in control group 30% patients were complete responders.
Conclusion: Hydrogel dressings appear to be more effective, safe, and patient satisfactory compared to conventional dressings for the treatment of Diabetic foot.
Downloads
References
2. Apelqvist J, Bakker K, van Houtum WH, Nabuurs-Franssen MH, Schaper NC. International consensus and practical guidelines on the management and the prevention of the diabetic foot. International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2000;16 Suppl 1:S84–S92.
3. Rathur HM, Boulton AJ. The diabetic foot. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:109–120. [PubMed]
4. Khanolkar MP, Bain SC, Stephens JW. The diabetic foot. QJM. 2008 Sep;101(9):685-95. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcn027. Epub 2008 Mar 18. [PubMed]
5. Queen D, Orsted H, Sanada H, Sussman G. A dressing history. Int Wound J. 2004 Apr;1(1):59-77. [PubMed]
6. Sibbald RG, Torrance G, Hux M, Attard C, Milkovich N. Cost-effectiveness of becaplermin for nonhealing neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2003 Nov;49(11):76-84. [PubMed]
7. Steed DL, Donohoe D, Webster MW, Lindsley L. Effect of extensive debridement and treatment on the healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetic Ulcer Study Group. J Am Coll Surg. 1996 Jul;183(1):61-4. [PubMed]
8. McDonald A, Lesage P. Palliative management of pressure ulcers and malignant wounds in patients with advanced illness. J Palliat Med. 2006 Apr;9(2):285-95. [PubMed]
9. Schultz GS, Sibbald RG, Falanga V, Ayello EA, Dowsett C, Harding K, Romanelli M, Stacey MC, Teot L, Vanscheidt W. Wound bed preparation: a systematic approach to wound management. Wound Repair Regen. 2003 Mar;11 Suppl 1:S1-28. [PubMed]
10. Trudgian J. Investigating the use of Aquaform Hydrogel in wound management. Br J Nurs. 2000 Jul 27-Aug 9;9(14):943-8. [PubMed]
11. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998 Sep 12;352(9131):837-53. [PubMed]
12. Lipsky BA. A report from the international consensus on diagnosing and treating the infected diabetic foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2004 May-Jun;20 Suppl 1:S68-77. [PubMed]
13. Lipsky BA, Berendt AR, Deery HG, Embil JM, Joseph WS, Karchmer AW, LeFrock JL, Lew DP, Mader JT, Norden C, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Oct 1;39(7):885-910. Epub 2004 Sep 10. [PubMed]
14. Vishwanathan V, Thomas N, Tandon N, Asirvatham A, Rajasekar S, Ramachandran A, Senthilvasan K, Murugan VS, Muthulakshmi Profile of diabetic foot complications and its associated complications - a multicentric study from India. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005;53:933–936.
15. Anandi C, Aaguraja D, Natarajan V, Ramanatham M, Subramaniam CS, Thulasiram M, Sumithra S. Bacteriology of diabetic foot lesions. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2004 Jul-Sep;22(3):175-8.
16. Gadepalli R, Dhawan B, Sreenivas V, Kapil A, Ammini AC, Chaudhry R. A clinico-microbiological study of diabetic foot ulcers in an Indian tertiary care hospital. Diabetes Care. 2006 Aug;29(8):1727-32. [PubMed]
17. Citron DM, Goldstein EJ, Merriam CV, Lipsky BA, Abramson MA. Bacteriology of moderate-to-severe diabetic foot infections and in vitro activity of antimicrobial agents. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:2819–2828. [PubMed]
18. Ramakant P, Verma AK, Misra R, Prasad KN, Chand G, Mishra A, Agarwal G, Agarwal A, Mishra SK. Changing microbiological profile of pathogenic bacteria in diabetic foot infections: time for a rethink on which empirical therapy to choose? Diabetologia. 2011;54:58–64. [PubMed]
19. Abdulrazak A, Bitar ZI, Al-Shamali AA, Mobasher LA. Bacteriological study of diabetic foot infections. J Diabetes Complications. 2005 May-Jun;19(3):138-41. [PubMed]
20. Raja NS. Microbiology of diabetic foot infections in a teaching hospital in Malaysia: a retrospective study of 194 cases. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2007 Feb;40(1):39-44. [PubMed]
21. Bansal E, Garg A, Bhatia S, Attri AK, Chander J. Spectrum of microbial flora in diabetic foot ulcers. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2008 Apr-Jun;51(2):204-8. [PubMed]
22. Singh SK, Gupta K, Tiwari S, Shahi SK, Kumar S, Kumar A, Gupta SK. Detecting aerobic bacterial diversity in patients with diabetic foot wounds using ERIC-PCR: a preliminary communication. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2009;8:203–208.
23. Tiwari S, Pratyush DD, Dwivedi A, Gupta SK, Rai M, Singh SK. Microbiological and clinical characteristics of diabetic foot infections in northern India. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2012 Apr 13;6(4):329-32. [PubMed]
24. McDonald A, Lesage P. Palliative management of pressure ulcers and malignant wounds in patients with advanced illness. J Palliat Med. 2006 Apr;9(2):285-95.
25. Schultz GS, Sibbald RG, Falanga V, Ayello EA, Dowsett C, Harding K, Romanelli M, Stacey MC, Teot L, Vanscheidt W. Wound bed preparation: a systematic approach to wound management. Wound Repair Regen. 2003 Mar;11 Suppl 1:S1-28. [PubMed]
26. Trudgian J. Investigating the use of Aquaform Hydrogel in wound management. Br J Nurs. 2000 Jul 27-Aug 9;9(14):943-8. [PubMed]
27. Richa Khemariya Prashant Khemariya Comparative evaluation of efficacy of pure collagen type I based modern dressing with conventional dressing in the treatment of burn and diabetic foot ulcer. Int.J.Curr.Res.Med.Sci.(2016).2(2):1-10.
28. Ali M. Lone, MS,1 Mohd I. Zaroo, Vacuum-assisted closure versus conventional dressings in the management of diabetic foot ulcers: a prospective case–control study Diabet Foot 2014; 5: 10.3402/dfa.v5.23345.
29. Ravari H, Modaghegh MH, Kazemzadeh GH, Johari HG, Vatanchi AM, Sangaki A, Shahrodi MV. Comparision of vacuum-asisted closure and moist wound dressing in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013 Jan;6(1):17-20. doi: 10.4103/0974-2077.110091. [PubMed]
30. Ali Z, Anjum A, Khurshid L, Ahad H, Maajid S, Dhar SA. Evaluation of low-cost custom made VAC therapy compared with conventional wound dressings in the treatment of non-healing lower limb ulcers in lower socio-economic group patients of Kashmir valley. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015 Dec 10;10:183. doi: 10.1186/s13018-015-0314-5.
31. Yarwood-Ross L, Dignon AM. NPWT and moist wound dressings in the treatment of the diabetic foot. Br J Nurs. 2012 Aug 9-Sep 12;21(15):S26, S28, S30-2.
32. Noha Amin, John Doupis Diabetic foot disease: From the evaluation of the “foot at risk” to the novel diabetic ulcer treatment modalities World J Diabetes. 2016 Apr 10; 7(7): 153–164. Published online 2016 Apr 10.
33. Dumville JC, O’Meara S, Deshpande S Hydrogel dressings for healing diabetic foot ulcers (Review) Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online) 9(9):CD009101 • May 2011.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

