A Comparative Study on flap necrosis following Karydakis Flap Reconstruction and Z-Plasty in Patients with Sacrococcygeal Pilonidal Disease – Our experience
Abstract
Aim: The purpose of this study was to evaluate patients with sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease (SPSD) who underwent the Karydakis procedure and Z plasty at our centre concerning the perioperative findings, late postoperative results and recurrence. P
atients and Methods: A total of 30 patients presenting with SPSD at our centre underwent Karydakis flap repair and Z plasty from May 2019 to June 2021. These patients were then followed up and evaluated concerning operative time, drain use, hospital stay, suture removal, complications, and recurrence. The adipocutaneous flap of Karydakis was devised to shift the natal cleft, while Z-plasty involves a fasciocutaneous flap.
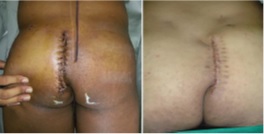
Results: The mean operative time was 60 min with a median hospital stay of 4 days. Drains were removed at a median of 5 days and sutures at a median of 15 days. The duration of hospitalisation for the Karydakis procedure was found significantly lesser than that for Z-plasty Patients who were followed up for a median of 12 months. The overall complications were more in Z-plasty. Flap necrosis developed in 30 % of the cases in the Z-plasty group, comparable to no recurrence seen in the Karydakis procedure.
Conclusion: Karydakis flap was found superior to Z-plasty, having less seroma formation, no flap necrosis and no local hematoma Karydakis flap procedure is a relatively simple procedure for SPSD and has advantages over Z-plasty technique like keeping scar away from the midline and flattening of the natal cleft, thus reducing local recurrence rates
Downloads
References
Bascom JU (1997) Procedures for pilonidal disease. In: Carter D, Russell RCG, Pitt HA (eds) Atlas of general surgery, 3rd edn. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 862–872.
Da Silva JH. Pilonidal cyst: cause and treatment. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000 Aug;43(8):1146-56. doi: 10.1007/BF02236564.
Søndenaa K, Andersen E, Nesvik I, Søreide JA. Patient characteristics and symptoms in chronic pilonidal sinus disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1995;10(1):39-42. doi: 10.1007/BF00337585.
Hull TL, Wu J. Pilonidal disease. Surg Clin North Am. 2002 Dec;82(6):1169-85. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(02)00062-2..
Bendewald FP, Cima RR. Pilonidal disease. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2007 May;20(2):86-95. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-977486
Karydakis GE. Easy and successful treatment of pilonidal sinus after explanation of its causative process. Aust N Z J Surg. 1992 May;62(5):385-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1992.tb07208.x.
McDermott FT. Pilonidal sinus treated by Z-plasty. Aust N Z J Surg. 1967 Aug 1;37(1):64-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1967.tb06989.x..
Chintapatla S, Safarani N, Kumar S, Haboubi N. Sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus: historical review, pathological insight and surgical options. Tech Coloproctol. 2003 Apr;7(1):3-8. doi: 10.1007/s101510300001
Khaled, M. Saad, and MS Awad Mohamed. Does closure of chronic pilonidal sinus still remain a matter of debate after bilateral rotation flap? (N-shaped closure technique). Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery 39.02 (2006): 157-162.
Awad MM, Elbaset AA, Ebraheem S, Tantawy E, Elhafez MA, Elsayed AM. A scoring system as a method to evaluate pilonidal sinus disease to make an easy decision for its management. Indian J Plast Surg. 2009 Jan-Jun;42(1):43-8. doi: 10.4103/0970-0358.53011
Monro Rs, Mcdermott Ft. The Elimination of Causal Factors In Pilonidal Sinus Treated By Z-Plasty. Br J Surg. 1965 Mar;52:177-81. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800520306. PMID: 14261120.
Senapati A, Cripps NP, Thompson MR. Bascom's operation in the day-surgical management of symptomatic pilonidal sinus. Br J Surg. 2000 Aug;87(8):1067-70. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.2000.01472.x.
Kitchen PR. Pilonidal sinus: excision and primary closure with a lateralised wound - the Karydakis operation. Aust N Z J Surg. 1982 Jun;52(3):302-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1982.tb05405.x.
Anyanwu AC, Hossain S, Williams A, Montgomery AC. Karydakis operation for sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease: experience in a district general hospital. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1998 May;80(3):197-9.
Karydakis GE. New approach to the problem of pilonidal sinus. Lancet. 1973 Dec 22;2(7843):1414-5. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92803-1.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


















 Therapoid
Therapoid

