Evaluation of Laboratory risk indicators (LRINEC Sore) for early diagnosis and prognosis in necrotizing fasciitis.
Bansal N.1*, Garg N.2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijoso.2020.i03.07
1* Neeraj Bansal, PG Resident, Department of General Surgery, Peoples College of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India.
2 Nitin Garg, Professor and HOD, Department of General Surgery, Peoples College of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India.
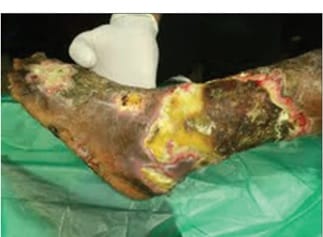
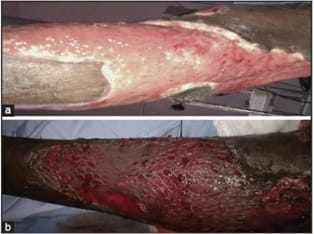
Background: Necrotizing soft tissue infections are rare but potentially fatal involving subcutaneous tissues and fascia. It can progress to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), shock, potential limb loss and death. The present study is an attempt to evaluate the early diagnostic efficacy and prognostic value of laboratory risk indicators (LRINEC scoring system) in necrotizing fasciitis. Methods: This prospective observational study was conducted onall patients of 18-80year age admitted in the Department of Surgery, PCMS and RC during the study period presenting with any of the clinical features of soft tissue infections.LRINEC SCORE was calculated for each patient using the laboratory values (CRP, WBC, Hb, sodium, creatinine and glucose) that ranged from 0-13Record was made of the final diagnosis and prognosis. Diagnostic and prognostic value of LRINEC score was evaluated using statistical analysis. Results: The most common site involved was Lower Extremities followed by Upper and Scrotum/Perineum. The study revealed that risk increases with advancing age. The systemic complication was in the intermediate and high-risk case, no one in low-risk case. The conservative treatment was mainly used for the patients with low risk but the surgical intervention was the mainstay of management in the intermediate and high-risk category. Conclusion: In the present study it can be concluded that LRINEC score, using readily available laboratory data, can serve as a simple and an important tool in predicting the prognosis and risk stratification in cases of necrotizing fasciitis but diagnostic efficacy is not that much reliable.
Keywords: Necrotizing Fasciitis, LRINEC Score, Soft Tissue Infection, Fasciotomy
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , PG Resident, Department of General Surgery, Peoples College of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India. Email: |
Bansal N, Garg N. Evaluation of Laboratory risk indicators (LRINEC Sore) for early diagnosis and prognosis in necrotizing fasciitis.. Surgical Rev Int J Surg Trauma Orthoped. 2020;6(3):181-188. Available From https://surgical.medresearch.in/index.php/ijoso/article/view/190 |


 ©
©