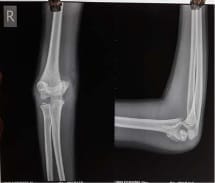
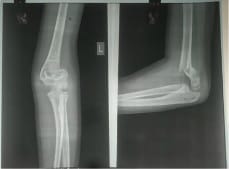
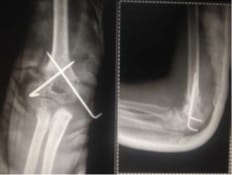
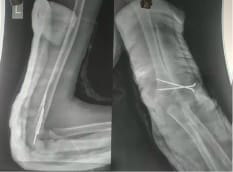
A study to evaluate the functional outcome of displaced supracondylar humerus fracture in pediatrics treated with closed reduction and k-wire fixation
Vora J.1, Patel B.2*, Vala G.3
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijoso.2020.i02.05
1 Jinesh Vora, Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, C U Shah Medical College and Hospital, Surendranagar, Gujarat, India.
2* Baiju Patel, 3rd Year Resident Doctor, Department of Orthopaedics, C U Shah Medical College and Hospital, Surendranagar, Gujarat, India.
3 Gaurav Vala, Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, C U Shah Medical College and Hospital, Surendranagar, Gujarat, India.
Introduction: Supracondylar fracture of the humerus is the most common elbow injury in children and makes up approximately 60% of all elbow injuries. The purpose of the present study is to evaluate the functional outcome of the displaced supracondylar humerus fracture treated with closed reduction and k-wire fixation by lateral and cross pinning technique. Material and Method: 50 children with fractures of the supracondylar humerus out of which 30 were boys and 20 were girls taken for prospective study at C.U. Shah Medical College from May 2017 to August 2019 was analyzed clinically and radiologically using Flynn’s criteria. Out of 50 cases 28 patients treated with lateral pinning and 22 patients treated with cross pinning technique based on the surgeon’s preference. Result: among patients treated with lateral pinning technique 19(68%) had an excellent result, 9(32%) had a good result. Similarly in patients treated with cross pinning technique, 9(41%), 7(32%), 2(9%), 4(18%) had excellent, good, fair, and poor outcomes respectively. 9 patients developed iatrogenic ulnar nerve palsy in cross pinning technique whereas 2 patients developed cubitus varus following cross pinning technique. Conclusion: Thus it can be concluded that closed reduction and K-wire fixation is an excellent method for the treatment of supracondylar fracture of the humerus with the significant difference in functional outcome between lateral pinning and cross pinning technique. The chances of ulnar nerve palsy increase following cross pinning technique which is not so in the case of lateral pinning. Thus suggesting the use of lateral pinning technique for the treatment of displaced supracondylar fracture of the humerus.
Keywords: Supracondylar fracture, Humerus, K-wire fixation
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , 3rd Year Resident Doctor, Department of Orthopaedics, C U Shah Medical College and Hospital, Surendranagar, Gujarat, India. Email: |
Vora J, Patel B, Vala G. A study to evaluate the functional outcome of displaced supracondylar humerus fracture in pediatrics treated with closed reduction and k-wire fixation. Surgical Review Int J Surg Trauma Orthoped. 2020;6(2):93-98. Available From https://surgical.medresearch.in/index.php/ijoso/article/view/158 |


 ©
©